Compression & Blow Moulding
Compression Moulding
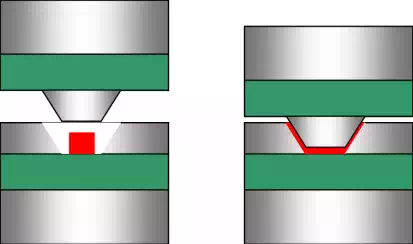
Compression moulding is principally used for thermosetting plastics.
Preheated resin is placed into a hot mould cavity. The upper section of the mould is subsequently forced down onto the resin to create the desired product shape. The applied pressure and heat forces the liquefied polymer to fill the cavity.
Following the compression, a period of heating is required to force cross-linking of the thermosetting polymer.
After Foundations of Materials Science and Engineering, William F. Smith, 3rd Edition, McGraw Hill
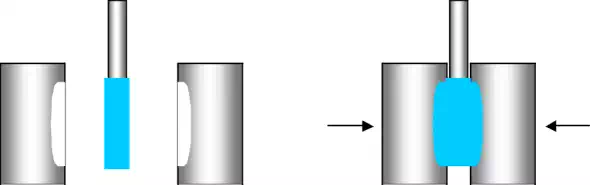
Blow Moulding
In blow moulding, a cylinder of plastic is placed inside a mould. One end of the cylinder is clamped shut and air is blown in from the other end to push the polymer against the walls of the of the mould. The air pressure is held constant as the part is cooled.
Blow moulding is generally used for containers such as PET (Poly(ethylene terephthalate)) bottles.