Injection & Extrusion
There are a number of different methods that are commonly used for forming of polymers. These methods rely to a large extent on whether the polymer is a thermoplastic or thermoset.
Thermoplastics are melted from a solid and reshaped before cooling. Common forming methods include injection moulding, blow moulding and extrusion.
Thermosets are not fully polymerised before forming. They are formed into the desired shape and then made into a solid through a chemical reaction to create cross-links in the polymer chains. Common forming methods include injection moulding, compression moulding and transfer moulding.
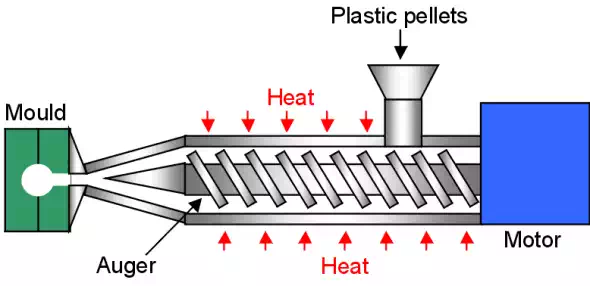
Injection Moulding
Injection moulding is by far the most important method of forming plastic materials.
Plastic pellets are fed into a rotating auger. The auger moves the pellets down a path towards the mould. As the pellets move they are pushed against the heated outer walls and are melted into a viscous liquid.
At the end of the moulding machine the polymer liquid is injected into a fashioned mould and cooled until solid.
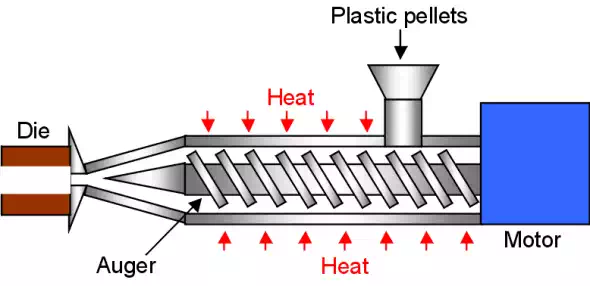
Extrusion
Extrusion is used for producing plastic parts that are generally simple and continuous in nature such as pipes and sheets.
The process is similar to injection moulding in that melted polymer is moved along by an auger. The polymer, however, is continually thread through an open die to form a continuous part with constant cross-sectional shape.