Verification Tests of Antimicrobial Finish
The types of test for verification of antimicrobial finish in our research work
is: Quantitative Test
Qualitative Test helps us to verify that whether antimicrobial finish is applied
properly on the substrate or not. The test that we commonly use on industrial
scale is known as “BPB (Bromo Phenol Blue)” Test. In this research Quantitative
test method has been followed Universal Beer Agar (UBA).
Result and Discussion of
Anti-Microbial Finish
In this chapter, antimicrobial activity of the treated fabric is investigated
against different concentration of Chitosan and turmeric
Below here we listed the results of effectiveness of antimicrobial
activity.
|
|
|
|
|
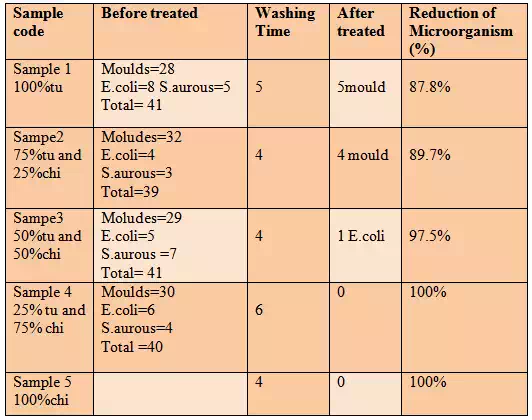
Table 4.1: Results of effectiveness of antimicrobial activity |
|
|
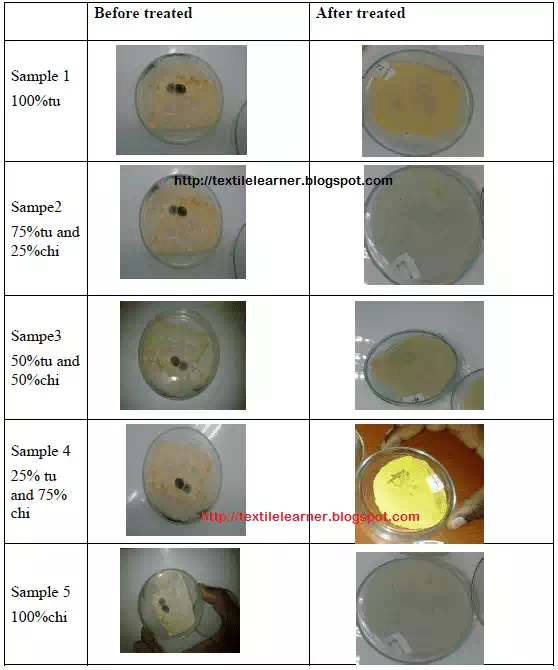
|
Table 4.2: Result of anti-microbial finish |
e.g. Sample 1 to calculate the
percentage reduction in standard time using
% Reduction = [(A-B)/A] x 100 41-1]/41 X 100 =87.8%
All the above sample are calculated by this methods
Discussion of Testing Results of Antimicrobial Activity
It is concluded from testing results of antimicrobial activity that sample like
1 has 100% amount of turmeric in their recipes. Amount was less when we compare
from the other samples (2, 3, 4&5). Even with in high washing time then we
concluded that it comes in the category of Under Treated.
Similarly when we compare Sample 2 from sample 1 then we concluded that it
comes in the category of slightly significant. In this recipe, amount of
Chitosan was 25% $ tumeric75%.
When we again compare Sample 3 with like’s sample 1$ 2 in these recipes, amount
of Chitosan was 50% $50% turmeric then we concluded that is more
significant.
Lastly when we camper sample 4$ 5there is no significant different between them
both are more effective anti-microbial activity.
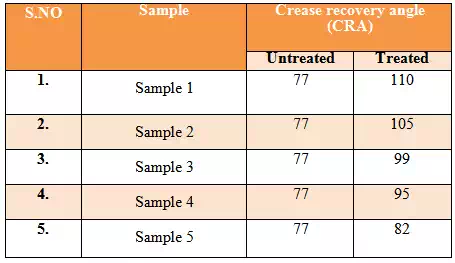
Crease recovery angle:
Crease recovery angle behaviour has been measured in terms of total crease
recovery angle (CRA), which is the sum of crease recovery angel measured in
warp and weft way CRA is only 77º for untreated fabric and for all treated the
value range from 82 º to 110 which is comparable to that of treated control
sample increase in the CRA is mainly due to cross linking of cellulose
chine.
As concentration of chitosan 100% treated samples show only a marginal increase
in crease recovery angle values in the range 82º- 95º, it inferred the chitosan
cannot improve crease recovery angel of cotton fabric significantly but,
addition of turmeric helps to improve the crease recovery though the molecular
cross liking and makes the fabric more functional. Almost all sample shows good
creases recover angel around 110º (table)
|
|
|
Table 4.3: Crease recovery angle |
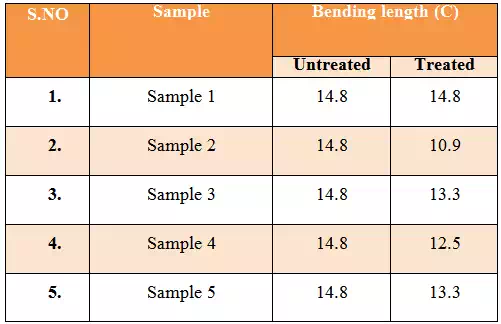
Bending length (C):
The bending length is related to the angle that the fabric makes to the
horizontal we calculate by using formula. when we compare Bending length (C) for
untreated fabric 14.8cm and 100% chitosan we conclude that the fabric is
stiffer, lack good drape, and lack flexibility. From treated one…….
|
|
|
Table 4.4: Bending length |
|
|
|
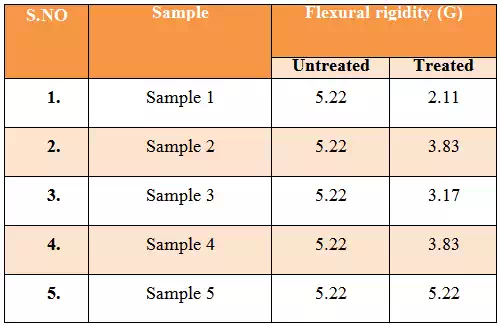
Table 4.5: Flexural rigidity |
Conclusions
The coating of cotton fabric using turmeric and chitosan natural product was
found to exhibit antibacterial properties. It exhibits efficient antimicrobial
agent for the preparation of antimicrobial finish of medical cloths. The
antibacterial efficacy of only turmeric and 75% turmeric combination with 25%
chitosan coated fabric was found to be less efficient compared to only chitosan
and 25tumeric combination with 75% chitosan coated fabric may be due to their
binding properties. The improvement in the anti microbial property may be due
to present of cationised amino group (–NH+3) in the chitosan and not influence
present of turmeric The present investigation highlighted that coated fabric
shows antibacterial properties against gram negative bacteria and gram positive
bacteria reports on the efficiency of indicating that this technique can be
used in the textile industry as antimicrobial finish of medical cloths both for
gram positive and gram negative bacteria as value added products.