SURFACE ORNAMENTATION
In the last three decades, Indian textile industry has witnessed drastic changes. The competitive atmosphere and quality consciousness, has reached a new mark. With the steady improvement in technology and application standards, a gradual rise was observed in consumer demands. And to reach up to that mark, a manufacturer has to add something to their products to get some added value for their product. This value added products not only reward with considerable increase in profit but also build the brand image. This part of the course introduces the students to the knowledge and skill of ornamenting the fabric for value addition. There are various techniques of adding value on textiles like embroidery, appliqué, patch work, dyeing, printing, etc.
EMBROIDERY
Embroidery is the art or handicraft of decorating fabric or other materials with needle and thread or yarn. There are different types of embroidery which are known by special names such as cut work, appliqué work, drawn thread work, smocking, etc. Embroidery may also incorporate other materials such as, pearls, beads, mirrors, metal strips, sequins, etc. Embroidery is done by hand and machine. Initially, wool, linen, and silk have been in use for thousands of years but today, embroidery is practiced with cotton, rayon, wool, silk, zari, etc.
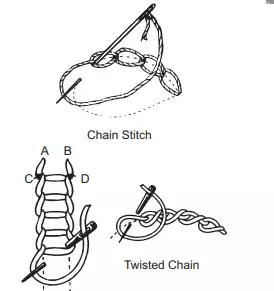
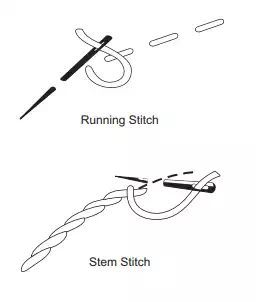
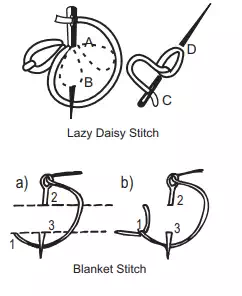
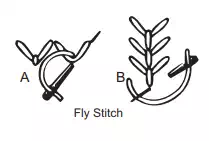
Common Embroidery Stitches
In general embroidery stitches are worked with two strands of embroidery skein. Sometimes more strands may be used for special effects. In the beginning and ending of the stitches avoid using knots. Begin with a back stitch leaving a short length of the thread(about 2 inches) extending on the wrong side which can be caught and held under the first few embroidery stitches. To end the work, take the thread to the wrong side and work a back stitch again.