What is GPS?

GPS receivers are generally used in smartphones, fleet management system, military etc. for tracking or finding location.
Global Positioning System (GPS) is a satellite-based system that uses satellites and ground stations to measure and compute its position on Earth.
GPS is also known as Navigation System with Time and Ranging (NAVSTAR) GPS.
GPS receiver needs to receive data from at least 4 satellites for accuracy purpose. GPS receiver does not transmit any information to the satellites.
This GPS receiver is used in many applications like smartphones, Cabs, Fleet management etc.

GPS receiver uses a constellation of satellites and ground stations to calculate accurate location wherever it is located.
These GPS satellites transmit information signal over radio frequency (1.1 to 1.5 GHz) to the receiver. With the help of this received information, a ground station or GPS module can compute its position and time.
GPS receiver receives information signals from GPS satellites and calculates its distance from satellites. This is done by measuring the time required for the signal to travel from satellite to the receiver.
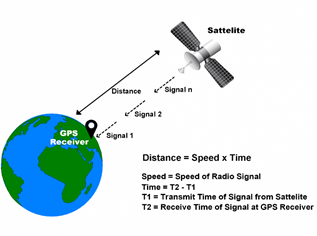
GPS Distance Calculation![]()
Where,
Speed = Speed of Radio signal which is approximately equal to the speed of light i.e.![]()
Time = Time required for a signal to travel from the satellite to the receiver.
By subtracting the sent time from the received time, we can determine the travel time.
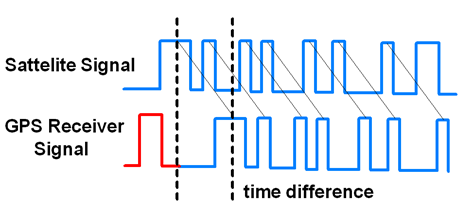
GPS Signal Time Difference
To determine distance, both the satellite and GPS receiver generate the same pseudocode signal at the same time.
The satellite transmits the pseudocode; which is received by the GPS receiver.
These two signals are compared and the difference between the signals is the travel time.
Now, if the receiver knows the distance from 3 or more satellites and their location (which is sent by the satellites), then it can calculate its location by using Trilateration method.

GPS Receiver
GPS receiver module gives output in standard (National Marine Electronics Association) NMEA string format. It provides output serially on Tx pin with default 9600 Baud rate.
This NMEA string output from GPS receiver contains different parameters separated by commas like longitude, latitude, altitude, time etc. Each string starts with ‘$’ and ends with carriage return/line feed sequence.
E.g.
$GPGGA,184237.000,1829.9639,N,07347.6174,E,1,05,2.1,607.1,M,-64.7,M,,0000*7D
$GPGSA,A,3,15,25,18,26,12,,,,,,,,5.3,2.1,4.8*36
$GPGSV,3,1,11,15,47,133,46,25,44,226,45,18,37,238,45,26,34,087,40*72
$GPGSV,3,2,11,12,27,184,45,24,02,164,26,29,58,349,,05,26,034,*7F
$GPGSV,3,3,11,21,25,303,,02,11,071,,22,01,228,*40
$GPRMC,184237.000,A,1829.9639,N,07347.6174,E,0.05,180.19,230514,,,A*64
Pin Description

GPS Receiver Module
VCC: Power Supply 3.3 – 6 V
GND: Ground
TX: Transmit data serially which gives information about location, time etc.
RX: Receive Data serially. It is required when we want to configure GPS module.
Before Interfacing GPS module with PIC18F4550 microcontroller, we can check the output of GPS module. From that string, we can extract information like longitude, latitude, time which is helpful to find location and timing information.
To do this, connect this GPS module to the PC via USB to Serial converter or DB9 connector. Also, it is necessary to keep antenna of GPS module on proper location.
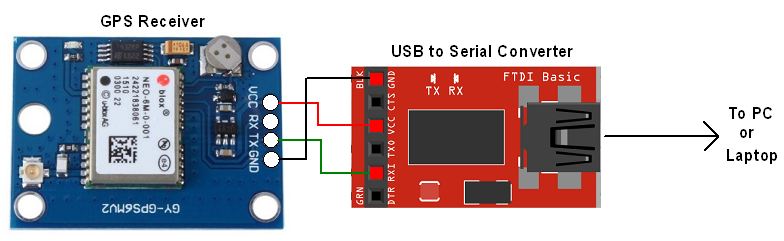
GPS Serial Interface
1. Now open any serial terminal e.g. Realterm, Hyper terminal, Putty etc. on PC/laptop.
2. Open the PORT with 9600 baud rate.
3. The terminal will show data coming from GPS receiver module.
The output data from GPS receiver module displaying on a serial terminal as follows.
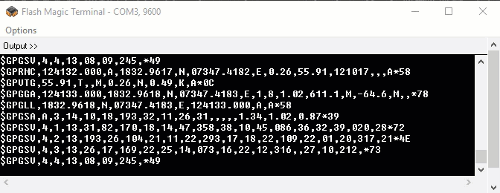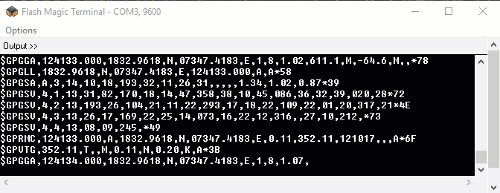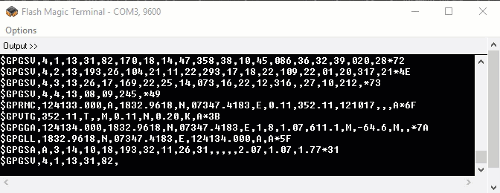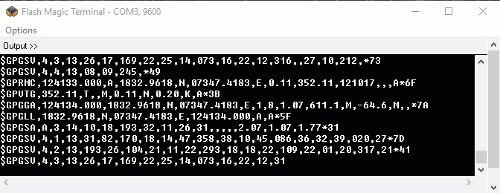
In the above string, the NMEA string starting with “$GPGGA” is most popularly used. It provides us Time, Longitude, Latitude and Altitude along with directions. This information is helpful to find Time and Location.
E.g.
$GPGGA,184241.000,1829.9639,N,07347.6174,E,1,05,2.1,607.1,M,-64.7,M,,0000*7C
Name | Example | Units | Description |
Message ID | $GPGGA |
| GGA Protocol Header |
UTC Time | 184241.000 |
| hhmmss.sss |
Latitude | 1829.9639 |
| ddmm.mmmm |
N/S Indicator | N |
| N=North, S=South |
Longitude | 07347.6174 |
| dddmm.mmmm |
E/W Indicator | E |
| E=East, W=West |
Position Fix Indicator | 1 |
| Fix GPS SPS mode |
Satellites Used | 05 |
| Range 0 to 12 |
HDOP | 2.1 |
| Horizontal Dilution of Precision |
MSL Altitude | 607.1 | Meters | Mean Sea Level |
Units | M | Meters |
|
Geoid Separation | 64.7 | Meters |
|
Units | M | Meters |
|
Age of Diff. Corr. | - |
| Null field if DGPS is not used |
Diff. Ref Station ID | 0000 |
|
|
Checksum | *7C |
|
|
Carriage return Line Feed | <CR><LF> |
| End of message transmission |