Synchronous Optical NETwork (SONET)
Synchronous optical networking (SONET) is a standardized digital communication protocol that synchronously transfers multiple data streams over long distances through fiber optic cables. It is a physical layer specification that allows simultaneous transmission of voice, data, and video at speeds as high as 1Gbps through a single fiber. In telephone networks, it is used for transmission of a huge amount of telephone calls and data streams through fiber.
SONET was standardized by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI). It is equivalent to Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH) standardized by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU).
The basic SONET frame comprises of a block of 810 bytes. The frames are transmitted at the rate of 8000 frames/bytes, which is the sampling rate of the telephone networks.
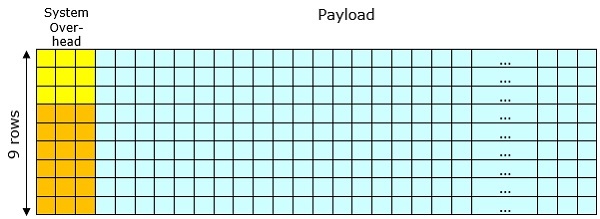
A SONET frame is represented as a rectangular block of bytes with 9 rows and 90 columns as shown in the following diagram.

The first three columns of the SONET frame contains the system information and is generally termed as system overhead, while the rest (marked in blue) contains the payload, i.e. the data to be transmitted. In this frame, the first three rows of the system overhead (marked in yellow) contain section overhead, and the nest six rows (marked in orange) contain line overhead.