Digital Subscriber Lines
Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) is a communication technology that offers high – bandwidth digital communication over standard telephone lines formed of copper wires.
· DSL is a family of technologies under the general name of xDSL, for various x, like ADSL, HDSL, and RADSL.
· Originally, it was a part of the Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) and was called IDSL.
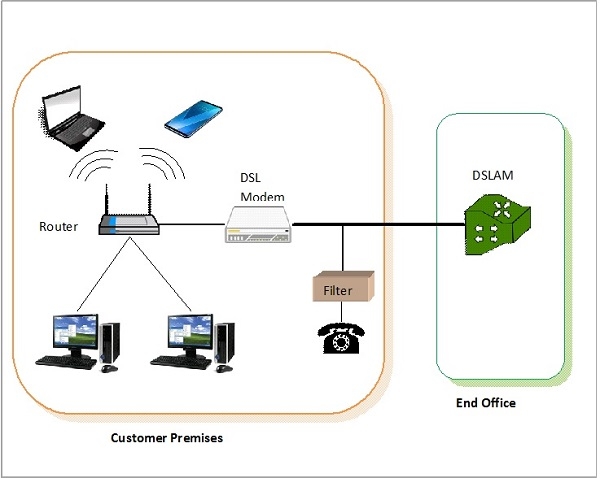
· DSL technology is used in the local loop of the telephone network, i.e. the part of the telephone network that connects the customer premises with the end office of the telephone company.
· Some DSL services provide more than the standard bandwidth of the telephone lines. These are called broadband services.
· DSL uses higher frequency bands for transmission of data in the range of 25 KHz to 1.5MHz. Voice transmission occurs at less than 4 KHz. So, data transmission occurs simultaneously with voice transmission.
· DSL filters are used on customer premises with non-DSL connections.
· DSL uses analog sinusoidal carrier waves for data transmission. The waves are modulated and demodulated at the customer premises with DSL modems.
· The telephone company uses a Digital Subscriber Line Access Multiplexer (DSLAM) at its end office so that multiple DSL users can be connected to the high-speed backbone network.
· Asymmetric DSL (ADSL)
· Consumer DSL (CDSL)
· DSL Lite
· High bit-rate DSL (HDSL)
· ISDN DSL (IDSL)
· Symmetric DSL (SDSL)
· Very high data rate DSL (VDSL)
Schematic Diagram of DSL Connection
