What is Digitization
Accuracy in communication is one of the most critical communication skills. It sounds so obvious and simple, yet this essential aspect of communication is often overlooked. The impact can be massive, for better or worse. This applies to both verbal and written communications. Accuracy in communication puts you and your listeners on the same page. Your message is clearly and accurately delivered. It is clearly and accurately received. The possibility of misunderstandings, misinterpretations and even poor decisions, is radically reduced. Consistent communications also make future conversations easier, because the definitions are concrete, discussions about misunderstandings and ambiguities are avoided, and trust is built.
Many people have begun to conflate terminology either out of ignorance or for their own benefit, which creates confusion, because suddenly we’re talking about different things but calling them the same. Some have begun labeling digitalization as digital transformation to appease management, get a project approved, or to make a sale. In this discussion, I hope to clarify the terminology and attempt to bring some baseline for discussions.

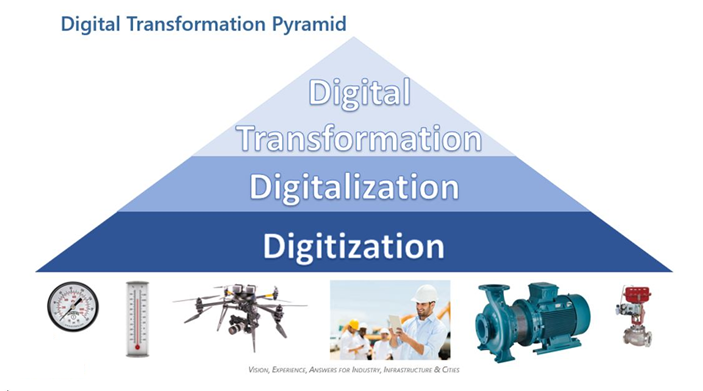
Let’s start with the term digitization. Digitization refers to creating a digital representation of physical objects or attributes. For instance, we scan a paper document and save it as a digital document (e.g., PDF). In other words, digitization is about converting something non-digital into a digital representation or artifact. Computerized systems can then use it for various use cases. An example from manufacturing would be when a measurement is converted from a manual or mechanical reading to an electronic one.
Digitization is foundational. This is the connection between the physical world and software. This is what we been doing since the 1960s. It is an enabler for all the processes that provide business value because of the need for consumable data.
Digitalization refers to enabling or improving processes by leveraging digital technologies and digitized data. Therefore, digitalization presumes digitization. Examples of this could be as simple as PLC logic or PID control in a microprocessor-based system, sequenced logic for a batch process, automated shutdown logic, etc. It could also be something more complex, like an error in a transmitter generating a work order in the ERP maintenance system for a maintenance tech.
Digitalization increases productivity and efficiency while reducing costs. Digitalization improves an existing business process or processes but doesn’t change or transform them. That is to say, it takes a process from a human-driven event or series of events to software-driven.
Digital Transformation is really business transformation enabled by digitalization. The “digital” moniker is a little bit of a misnomer because the essence of digital transformation is the changing of business processes enabled or forced by digitalization technologies.
One example of this is the convergence of IT/OT where the intersection and overlap of IT skills within the OT domain has created the need for a more uniform governance due to cybersecurity concerns, data flow requirements, and skills. Another example of digital transformation is a shift from local control of physical processes to remote monitoring and control of those same processes. A more ambitious example would be the integration of your customer sales volumes feeding though to your company’s raw material vendors, thus integrating the supply chain for greater efficiency and response.
So, what is Industry 4.0 then? You can think of Industry 4.0 as being European for the combination of Digital Transformation and Digitalization, which kind of leads to a confusion all its own.
I would like to take a moment to share with you that there is a user community focused on topics similar to this. Please take this opportunity to check out and join this community called the Digital Transformation Council. This is a collaborative group of end user professionals who meet to exchange ideas and learn how digital transformation affects their companies, how to affect change within their companies, learn about failings and successes, etc. It is free to join and open to anyone in your organization.