Circuit-switched vs Packet-switched networks
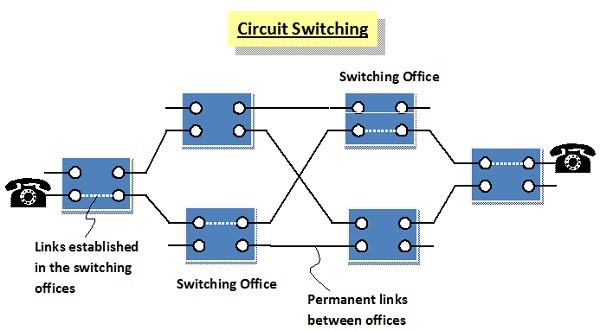
Circuit Switched Networks − Circuit switched networks are connection-oriented networks. Here, a dedicated route is established between the source and the destination and the entire message is transferred through it.
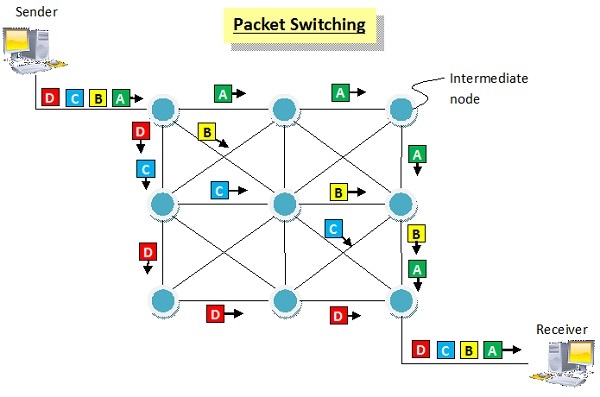
Packet Switched Networks − Packet switched networks are connectionless networks. Here, the message is divided and grouped into a number of units called packets that are individually routed from the source to the destination.
Differences with respect to technology
Serial Number | Circuit – Switching | Packet – Switching |
1 | It is a connection oriented network switching technique. | It is a connectionless network switching technique. |
2 | A dedicated path has to be established between the source and the destination before transfer of data commences. Once, the data is transmitted, the path is relinquished. | There is no need to establish a dedicated path from the source to the destination. |
3 | It is inflexible in nature since data packets are routed along the same dedicated path. | Each packet is routed separately. Consequently, it is flexible in nature where the different data packets follow different paths. |
4 | It was initially designed for voice transfer. | It was initially designed for data transfer. |
5 | The entire message is received in the order sent by the source. | The individual packets of the message are received out of order and so need to be reassembled at the destination. |
6 | It is implemented at Physical Layer. | It is implemented at Network Layer. |
7 | It has two approaches −
| It has two approaches −
|
8 | It is not a store and forward transmission. | It is store and forward transmission. |
9 | Data is processed and transmitted at the source only. | Data is processed and transmitted, not only at the source but at each switching station. |
Differences with respect to applicability, advantages and disadvantages.
Serial Number | Circuit – Switching Networks | Packet – Switching Networks |
1 | They are suitable for long continuous transmission, like voice calls. | They are unsuitable for applications that cannot afford delays in communication like high quality voice calls. |
2 | Once a route is established between the source and the destination, the route cannot be used by any other user. This leads to poor utilization of resources. | It allows simultaneous usage of the same channel by multiple users. This guarantees better resource utilization. |
3 | Bandwidth requirement is high even in cases of low data volume. | It ensures better bandwidth usage as a number of packets from multiple sources can be transferred via the same link. |
4 | Time required to establish connection may be high. | Delay in delivery of packets is less, since packets are sent as soon as they are available. |
5 | Initial cost is low. | Packet switching high installation costs. |
6 | The protocols for delivery are relatively simpler. | They require complex protocols for delivery. |
7 | It is more reliable. | It is less reliable. |