
What is parallel transmission?
When data is sent using parallel data transmission, multiple data bits are transmitted over multiple channels at the same time. This means that data can be sent much faster than using serial transmission methods.

Example of Parallel Data Transmission
Given that multiple bits are sent over multiple channels at the same time, the order in which a bit string is received can depend on various conditions, such as proximity to the data source, user location, and bandwidth availability. Two examples of parallel interfaces can be seen below. In the first parallel interface, the data is sent and received in the correct order. In the second parallel interface, the data is sent in the correct order, but some bits were received faster than others.
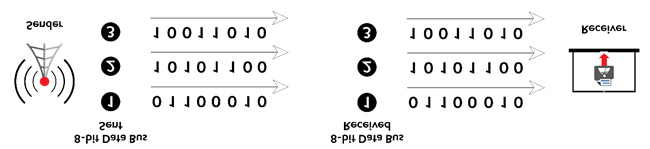
Example of Parallel Transmission – Data Received Correctly
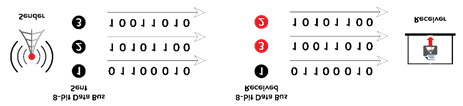
Example of Parallel Transmission – Data Received Incorrectly
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Parallel Data Transmission
The main advantages of parallel transmission over serial transmission are:
Although parallel transmission can transfer data faster, it requires more transmission channels than serial transmission. This means that data bits can be out of sync, depending on transfer distance and how fast each bit loads. A simple of example of where this can be seen is with a voice over IP (VOIP) call when distortion or interference is noticeable. It can also be seen when there is skipping or interference on a video stream.
When is parallel transmission used to send data?
Parallel transmission is used when:
A scenario where parallel transmission is used to send data is video streaming. When a video is streamed to a viewer, bits need to be received quickly to prevent a video pausing or buffering. Video streaming also requires the transmission of large volumes of data. The data being sent is also time-sensitive as slow data streams result in poor viewer experience.