What is serial transmission?
When data is sent or received using serial data transmission, the data bits are organized in a specific order, since they can only be sent one after another. The order of the data bits is important as it dictates how the transmission is organized when it is received. It is viewed as a reliable data transmission method because a data bit is only sent if the previous data bit has already been received.

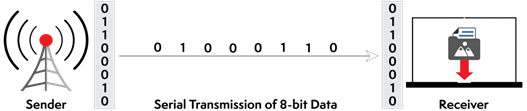
Example of Serial Data Transmission
Serial transmission has two classifications: asynchronous and synchronous.
Asynchronous Serial Transmission
Data bits can be sent at any point in time. Stop bits and start bits are used between data bytes to synchronize the transmitter and receiver and to ensure that the data is transmitted correctly. The time between sending and receiving data bits is not constant, so gaps are used to provide time between transmissions.
The advantage of using the asynchronous method is that no synchronization is required between the transmitter and receiver devices. It is also a more cost effective method. A disadvantage is that data transmission can be slower, but this is not always the case.
Synchronous Serial Transmission
Data bits are transmitted as a continuous stream in time with a master clock. The data transmitter and receiver both operate using a synchronized clock frequency; therefore, start bits, stop bits, and gaps are not used. This means that data moves faster and timing errors are less frequent because the transmitter and receiver time is synced. However, data accuracy is highly dependent on timing being synced correctly between devices. In comparison with asynchronous serial transmission, this method is usually more expensive.
When is serial transmission used to send data?
Serial transmission is normally used for long-distance data transfer. It is also used in cases where the amount of data being sent is relatively small. It ensures that data integrity is maintained as it transmits the data bits in a specific order, one after another. In this way, data bits are received in-sync with one another.