What is Data Transmission?
Definition Data Transmission: When we enter data into the computer via keyboard, each keyed element is encoded by the electronics within the keyboard into an equivalent binary coded pattern, using one of the standard coding schemes that are used for the interchange of information. To represent all characters of the keyboard, a unique pattern of 7 or 8 bits in size is used. The use of 7 bits means that 128 different elements can be represented, while 8 bits can represent 256 elements. A similar procedure is followed at the receiver that decodes every received binary pattern into the corresponding character.
The most widely used codes that have been adopted for this function are the Extended Binary Coded Decimal (EBCDIC) and the American Standard Code for Information Interchange codes (ASCII). Both coding schemes cater to all the normal alphabetic, numeric, and punctuation characters, collectively referred to as printable characters and a range of additional control characters, known as non-printable characters.
Data transmission refers to the movement of data in form of bits between two or more digital devices.
This transfer of data takes place via some form of transmission media (for example, coaxial cable, fiber optics etc.)
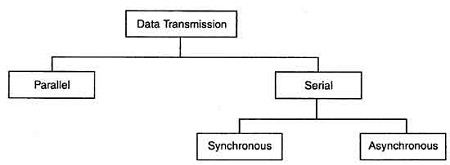
Types of Data Transmission
