Generally, networks are distinguished based on their geographical span. A network can be as small as distance between your mobile phone and its Bluetooth headphone and as large as the internet itself, covering the whole geographical world,
A Personal Area Network (PAN) is smallest network which is very personal to a user. This may include Bluetooth enabled devices or infra-red enabled devices. PAN has connectivity range up to 10 meters. PAN may include wireless computer keyboard and mouse, Bluetooth enabled headphones, wireless printers and TV remotes.

For example, Piconet is Bluetooth-enabled Personal Area Network which may contain up to 8 devices connected together in a master-slave fashion.
A computer network spanned inside a building and operated under single administrative system is generally termed as Local Area Network (LAN). Usually,LAN covers an organization’ offices, schools, colleges or universities. Number of systems connected in LAN may vary from as least as two to as much as 16 million.
LAN provides a useful way of sharing the resources between end users.The resources such as printers, file servers, scanners, and internet are easily sharable among computers.
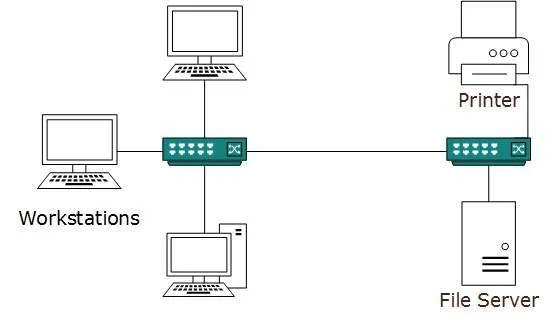
LANs are composed of inexpensive networking and routing equipment. It may contains local servers serving file storage and other locally shared applications. It mostly operates on private IP addresses and does not involve heavy routing. LAN works under its own local domain and controlled centrally.
LAN uses either Ethernet or Token-ring technology. Ethernet is most widely employed LAN technology and uses Star topology, while Token-ring is rarely seen.
LAN can be wired,wireless, or in both forms at once.
The Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) generally expands throughout a city such as cable TV network. It can be in the form of Ethernet,Token-ring, ATM, or Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI).
Metro Ethernet is a service which is provided by ISPs. This service enables its users to expand their Local Area Networks. For example, MAN can help an organization to connect all of its offices in a city.
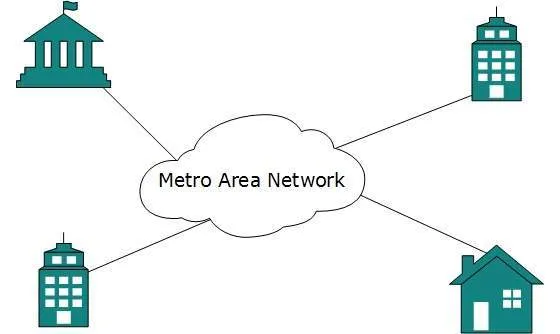
Backbone of MAN is high-capacity and high-speed fiber optics. MAN works in between Local Area Network and Wide Area Network. MAN provides uplink for LANs to WANs or internet.
As the name suggests,the Wide Area Network (WAN) covers a wide area which may span across provinces and even a whole country. Generally, telecommunication networks are Wide Area Network. These networks provide connectivity to MANs and LANs. Since they are equipped with very high speed backbone, WANs use very expensive network equipment.
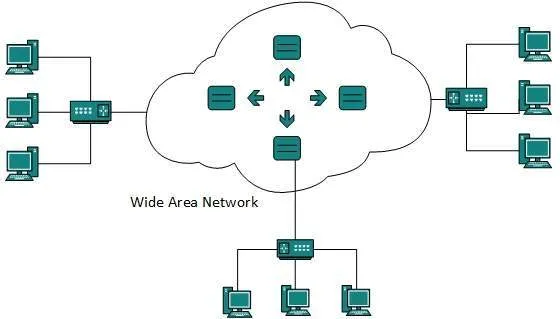
WAN may use advanced technologies such as Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM), Frame Relay, and Synchronous Optical Network (SONET). WAN may be managed by multiple administration.
A network of networks is called an internetwork, or simply the internet. It is the largest network in existence on this planet.The internet hugely connects all WANs and it can have connection to LANs and Home networks. Internet uses TCP/IP protocol suite and uses IP as its addressing protocol. Present day, Internet is widely implemented using IPv4. Because of shortage of address spaces, it is gradually migrating from IPv4 to IPv6.
Internet enables its users to share and access enormous amount of information worldwide. It uses WWW, FTP, email services, audio and video streaming etc. At huge level, internet works on Client-Server model.
Internet uses very high speed backbone of fiber optics. To inter-connect various continents, fibers are laid under sea known to us as submarine communication cable.
Internet is widely deployed on World Wide Web services using HTML linked pages and is accessible by client software known as Web Browsers. When a user requests a page using some web browser located on some Web Server anywhere in the world, the Web Server responds with the proper HTML page. The communication delay is very low.
Internet is serving many proposes and is involved in many aspects of life. Some of them are: