SNR Considerations
The signal strength is determined by the EMF induced from each voxel due to the processing moments. The magnetic moment density is proportional to the polarizing field B0. Recall that the EMF is proportional to the rate of change of the coil flux. The derivative operation multiples the signal by the Larmor frequency, which is proportional to B0, so the received signal is proportional to B2 0 times the volume of the voxel Vv .
In a well-designed MRI system, the dominant noise source is due to thermally generated currents within the conductive tissues of the body. These currents create a time-varying flux which induces noise voltages in the receiver coil. Other noise sources include the thermal noise from the antenna and from the first amplifier. These subsystems are designed so that the noise is negligible compared with the noise from the patient. The noise received is determined by the total volume seen by the antenna pattern Vn and the effective resistivity and temperature of the conductive tissue. One can show that the standard deviation of the noise from conductive tissue varies linearly with B0. The noise is filtered by an integration over the total acquisition time Tacq, which effectively attenuates the noise standard deviation by √ (Tacq)Therefore, the SNR varies as
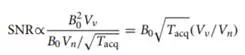
The noise volume Vn is the effective volume based on the distribution of thermally generated currents. For example, when imaging a spherical object of radius r, the noise standard deviation varies as r 5/2 . The effective resistance depends strongly on the radius because currents near the outer radius contribute more to the noise flux seen by the receiver coil.
To significantly improve the SNR, most systems use surface coils, which are simply small coils that are just big enough to see the desired region of the body. Such a coil effectively maximizes the voxel-volume to noise-volume ratio. The noise is significantly reduced because these coils are sensitive to currents from a smaller part of the body. However, the field of view is somewhat limited, so “phased arrays” of small coils are now being offered by the major manufacturers. In the phased array, each coil sees a small noise volume, while the combined responses provide the wide coverage at a greatly improved SNR.