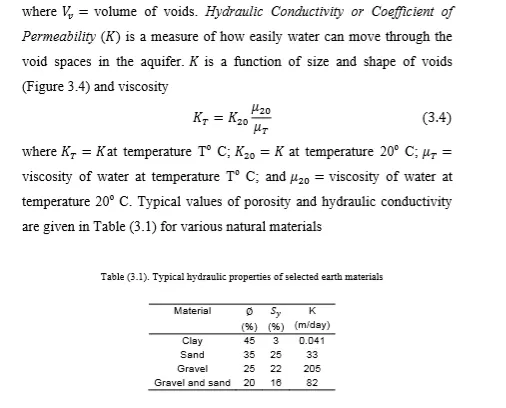
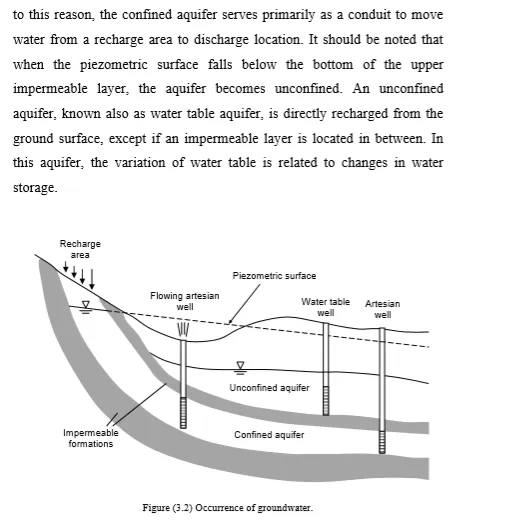
Occurrence of Groundwater

The hydraulic properties of an aquifer may vary spatially according to geological conditions. For example, not all the water can be drained by gravity or by a pumped well as part of it is held by surface tension, which is a water property influenced by soil texture. Estimation of these properties allows quantitative prediction of hydraulic response of aquifer to recharge and pumping processes. Therefore, it is important initially to define parameters describing the hydraulic properties of the aquifer. Storage Coefficient or Storativity relates the change in water volume within the storage of the aquifer per unit surface area of aquifer per unit decline of hydraulic head (Figure 3.3). In unconfined aquifer, water is stored in the void spaces and, thus, changes in storage are followed by variations in the elevation of the water table. In confined aquifer, water is stored with regard to earth material matrix (soil and water) compressibility, and changes in storage are followed by variations in piezometric surface. The storage coefficient is an indirect aquifer property that cannot be measured directly, but it can be estimated from pumping tests or from groundwater variation due to atmospheric pressure