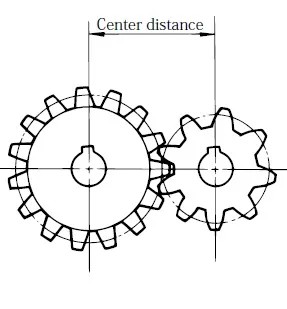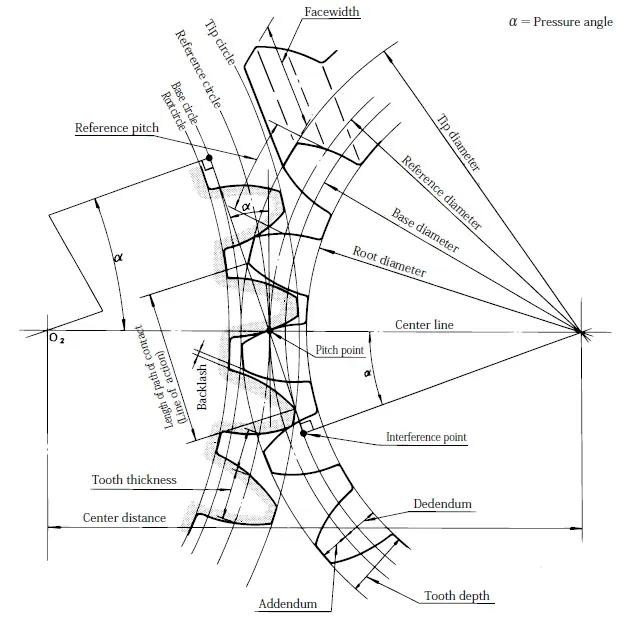
Important Gear Terminology in this picture :
Gear Terminology

Important Gear Terminology in this picture :
![]() Center distance
Center distance
![]() Length of path of contact (Line of action)
Length of path of contact (Line of action)
![]() Backlash
Backlash
![]() Interference point
Interference point
![]() Pitch point
Pitch point
![]() Reference pitch
Reference pitch
![]() Center line
Center line
![]() Tip circle
Tip circle
![]() Base circle
Base circle
![]() Root circle
Root circle
![]() Tip diameter
Tip diameter
![]() Reference diameter
Reference diameter
![]() Base diameter
Base diameter
![]() Root diameter
Root diameter
![]() Pressure angle
Pressure angle
![]() Face width
Face width
![]() Tooth depth
Tooth depth
![]() Addendum
Addendum
![]() Dedendum
Dedendum
![]() Tooth thickness
Tooth thickness
Gear Module
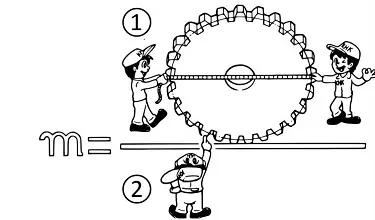
Module” is the unit of size that indicates how big or small a gear is. It is the ratio of the reference diameter of the gear divided by the number of teeth. Thus m = d/z (Module = Reference diameter/Number of teeth)
The mutual relation between the module and the reference diameter, etc. is as follows :
Reference diameter d = mz (Reference diameter = Module × Number of teeth)
Number of teeth z = d/m (Number of teeth = Reference diameter / Module)
Reference pitch p = πm (Reference pitch = π x module)
Then, what is the reference pitch ?
It is equal to the circumference divided by the number of teeth.
Reference pitch = Circumference (πd) / Number of teeth (z)
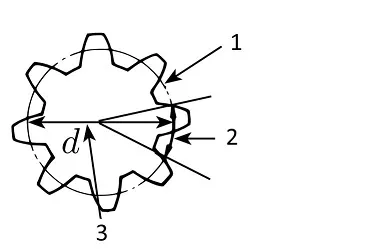
Then, what is the reference circle ?
Assume that there are two friction pulleys in contact whose diameters are equal to the reference diameters. As the surfaces are smooth, the rotation will not go properly when great force is applied. This problem will be solved if there are teeth on the periphery of the friction pulley. And this is the concept of gearing.
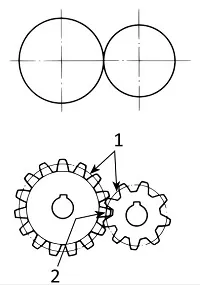
Summary
(1) The module describes the size of a gear.
(2) A pair of gears can only mesh correctly if and when the base pitch is the same.
Practicing What You’ve Learned
Spur Gear
Module m = 3
Pinion z1 = 15
Gear z2 = 55
Helical Gear
Module m = 3
Pinion z1 = 15
Gear z2 = 55
Helix angle β = 16º15′ / then cosβ = 0.96