
Power Transmitted by Ropes
Rope drive

The rope drive is widely used where a large amount of power is to be transmitted, from one pulley to another, over a considerable distance. Rope drives use a number of circular section ropes, rather than a single flat or vee belt.
It may be noted that the use of flat belts is limited for the transmission of moderate power from one pulley to another when the two pulley is not more than 8 metres apart.
One of the main advantages of rope drive is that a number of drives may take from the one driving pulley. Rope drives were most widely used as power transmission in mills and factories

Sheave for Ropes
· The diameter of the sheaves should be large to reduce the wear on the rope due to internal friction and bending stresses.
· The proper size of sheave wheels is 40 d and the minimum size is 36 d.
Types Of Ropes
The rope drive uses the following two types of ropes:
![]() Fibre Ropes
Fibre Ropes
![]() Wire ropes.
Wire ropes.
The fibre ropes operate successfully when the pulleys are about 60 metres apart, While the wire ropes are used when the pulleys are up to 150 metres apart.
Fibre Ropes
The ropes for transmitting power are usually made from fibrous, materials such as hemp, manila and cotton. Since the hemp and manila fibres are rough, Therefore the ropes made from these fibres are not very flexible and possesses poor mechanical properties.
The hemp ropes have less strength as compared to manila ropes. When the hemp and manila ropes are bent over the sheave (or pulley), there is some sliding of fibres, causing the rope to wear. In order to minimize this defect, the rope fibres are lubricated. The lubrication also makes the rope Moisture proof.
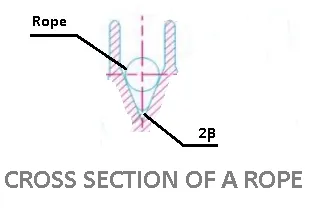
The fibre ropes are usually circular in cross-section. The groove angle of the pulley for rope drives is usually 45°. The grooves in the pulley are made narrow at the bottom and the rope is pinched between the edges of the v-groove to increase the holding power of the rope on the pulley.
Wire Ropes

When a large amount of power is to be transmitted over long distances from one pulley to another (i.e.when the pulleys are up to 150 metres apart), then wire ropes are used.
The wire ropes are widely used in elevators, mine hoists, cranes, conveyors, hauling devices and suspension bridges. The wise ropes run on grooved pulleys but they rest on the bottom of the grooves and are not wedged between the sides of the grooves.
The wire ropes have the following advantage over cotton ropes.
v Wire ropes are lighter in weight,
v these offer silent operation,
v These can withstand shock loads.
v Wire ropes are more reliable,
v They do not fail suddenly, These are more durable,
v The efficiency is high
v Less expensive or low in cost