Kinematic Chains, Joints, Degree of Freedom
KINEMATICS CHAINS
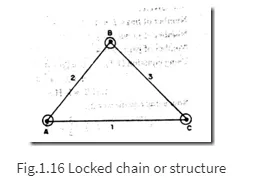
Kinematic chain: A kinematic chain is a group of links either joined together or arranged in a manner that permits them to move relative to one another. If the links are connected in such a way that no motion is possible, it results in a locked chain or structure.

TYPES OF JOINTS
The usual types of joints in a chain are
· Binary joint
· Ternary joint
· Quaternary joint
Binary Joint: If two links are joined at the same connection; it is called a binary joint. For example. Fig. 1.17 shows a chain with two binary joints named B.
Ternary Joint: If three links are joined at a connection, it is known as a ternary joint. It is considered equivalent to two binary joints since fixing of any one link constitutes two binary joints with each of the other two links. In Fig. 1.17 ternary links are mentioned as T.
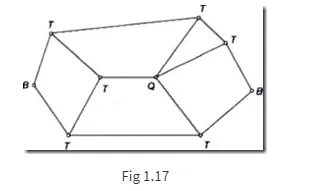
Quaternary Joint: If four links are joined at a connection, it is known as a quaternary joint. It is considered equivalent to three binary joints since fixing of any one link constitutes three binary joints. Figure 1.17 shows one quaternary joint.
In general, if ‘n’ number of links are connected at a joint, it is equivalent to (n-1) binary joints.
DEGREE OF FREEDOM
Degrees of freedom (DOF): It is the number of independent coordinates required to describe the position of a body in space. A free body in space (fig 1.18) can have six degrees of freedom. i.e., linear positions along x, y and z axes and rotational/angular positions with respect to x, y and z axes.
In a kinematic pair, depending on the constraints imposed on the motion, the links may lose some of the six degrees of freedom.

Possible Motions:
· Three translations along x, y and z axes.
· Three rotations about x, y and z axes.
So an object in free space has six degrees of Freedom.
A fixed object has zero degree of freedom.