
The mechanical and electrical parameters that characterize a DC Motor and play a crucial role in selection of the right motor are current rating, torque, power and motor efficiency. The big problem is how to calculate these parameters?
Let us walk you through the method we use to do these calculations.
When we purchase a motor from the market, we only get it's voltage and speed ratings. To design the driver circuit for this motor, we need to be able to supply current matching it's current ratings at the rated motor voltage.
Finding the Current Rating of a DC Motor
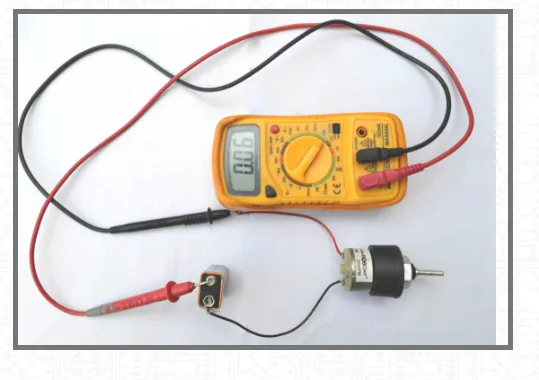
Connect negative terminal of a battery which gives voltage at the rated voltage level of the DC motor to any terminal of the motor. Now, connect a multimeter to the motor and battery as per the set up shown below. Ensure multimeter is set in current measurement mode. If the connections are done properly, the motor shall start running and current rating of the motor shall be displayed on the screen of multimeter.

Finding the Energy Consumption of a DC Motor
Electrical energy consumed by an electrical device is defined by the following formula:
Eelect = Pin * t
= I * V * t Where,
Eelect – Electrical energy consumed by the motor, measured in Watt-hour
Pin – Electrical Power consumed by the motor
I – current, measured in amperes (A)
V – applied voltage, measured in volts (V) t - Time for which motor runs in Hours
Once, we have the voltage and current ratings of the motor, it is easy to calculate the electrical energy consumed by it.
Calculating mechanical output power of a DC motor
Motors are supposed to do some work and two important values that define how powerful the motor is are motor speed and torque (turning force of the motor). Output mechanical power of the motor can be calculated by using the following formula:
Pout = τ * ω
Where,
Pout – output power, measured in watts (W)
τ – torque, measured in Newton meters (Nm)
ω – angular speed, measured in radians per second (rad/s).
It is easy to calculate angular speed if you know rotational speed of the motor in rpm:
ω = rpm * 2π / 60
Where,
ω – angular speed, measured in radians per second (rad/s)
rpm – rotational speed in revolutions per minute
π – mathematical constant pi (3.14).
60 – Number of seconds in a minute
Measuring the torque of the motor is a challenging task. It requires special expensive equipment. Therefore we suggest calculating it.
Efficiency E of the motor is calculated as mechanical output power divided by electrical input power:
In the above formula all of the value are known except efficency of the DC motor. Efficiency of commercially available DC motors ranges from 15 to 20%.
With this, torque as well as the output mechanical power of the motor can be calculated.
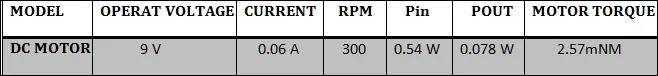
Example: - Consider a 9V / 300 RPM DC motor
Taking efficiency = 0.15
Torque τ = I * V * E * 60/2*π * N
= 0.06 *9 *0.15 *60 / 300 *2 *3.14
= 0.0025729 N-M
= 2.57 milliNewton-m
Output mechanical power Pout = τ * ω
= 0.0025729 * 2 * 3.14 * 300 / 60
= 0.078 w
Different parameters of the given DC motor can be tabulated as follows:
