Classification of textile fibres
Let us see how fibres are classified According to the source from which textile fibres are obtained fibres are broadly classified into two ways.
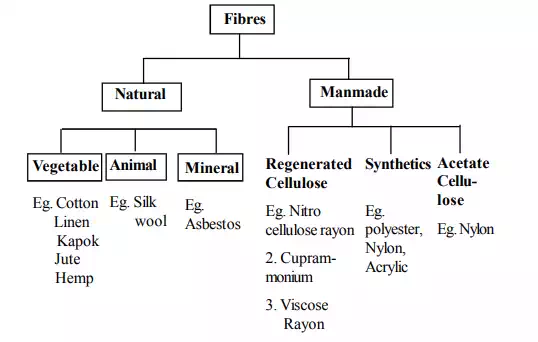
Vegetable fibres or cellulosic fibres
The fibres that are derived from plants are called vegetable fibres. The basic material of all plant life is cellulose. Cellulose is made up of elements like carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. These cellulose fibres have certain common properties like low resilience, high density, and good conductor of heat. They are highly absorbent and are resistant to high temperature. Cotton flax, jute, ramie are some of the examples of vegetable fibres.
Animal fibres
The fibres which are obtained from animals are called animal fibres. Wool and silk are common examples of animal fibres. They are made up of protein molecules. The basic elements in the protein molecules are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen. Animal fibres have high resiliency but weak when wet because they are bad conductors of heat.
Mineral fibres
They are the inorganic materials shaped in to fibres and are mainly used in the fire proof fabrics. Asbestos is the example of mineral fibre. Mineral fibres are fire proof, resistant to acids and are used for industrial purposes.
Man made fibres
These refer to those fibres that are not naturally present in nature and are made artificially by man. Man made fibres have high strength, strong when wet low moisture absorption characteristics. Examples of man made fibres are viscose rayon, acetate rayon, nylon, polyester etc. Depending on raw material chosen for making of the fibres they are classified as cellulosic fibres, protein fibres and synthetic fibres