
Flat fading
Fading basics | types of Fading in wireless communication
This page describes Fading basics and types of fading in wireless communication. The Fading types are divided into large scale fading and small scale fading (multipath delay spread and doppler spread). Flat fading and frequency selecting fading are part of multipath fading where as fast fading and slow fading are part of doppler spread fading. These fading types are implemented as per Rayleigh, Rician, Nakagami and Weibull distributions or models.
Introduction:
As we know wireless communication system consists of transmitter and receiver. The path from transmitter to the receiver is not smooth and the transmitted signal may go through various kinds of attenuations including path loss, multipath attenuation etc. The signal attenuation through the path depends on various factors. They are time, radio frequency and path or position of transmitter/receiver. The channel between transmitter and receiver can be time varying or fixed depending upon whether the transmitter/receiver are fixed or moving with respect to each other.
What is fading?
The time variation of received signal power due to changes in transmission medium or paths is known as fading. Fading depends on various factors as mentioned above. In fixed scenario, fading depends on atmospheric conditions such as rainfall, lightening etc. In mobile scenario, fading depends on obstacles over the path which are varying with respect to time. These obstacles create complex transmission effects to the transmitted signal.

The figure-1 depicts amplitude versus distance chart for slow fading and fast fading types which we will discuss later.
Fading types
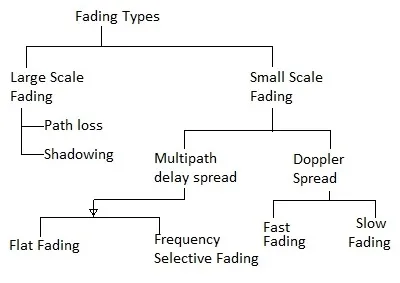
Considering various channel related impairments and position of transmitter/receiver following are the types of fading in wireless communication system.
➤Large Scale Fading: It includes path loss and shadowing effects.
➤Small Scale Fading: It is divided into two main categories viz. multipath delay spread and doppler spread. The multipath delay spread is further divided into flat fading and frequency selective fading. Doppler spread is divided into fast fading and slow fading.
➤Fading models: Above fading types are implemented in various models or distributions which include Rayleigh, Rician, Nakagami, Weibull etc.
As we know, fading signals occur due to reflections from ground and surrounding buildings as as well as scattered signals from trees, people and towers present in the large area. There are two types of fading viz. large scale fading and small scale fading.
1.) Large Scale Fading
Large scale fading occurs when an obstacle comes in between transmitter and receiver. This interference type causes significant amount of signal strength reduction. This is because EM wave is shadowed or blocked by the obstacle. It is related to large fluctuations of the signal over distance.
1.a) Path loss
The free space path loss can be expressed as follows.
➤ Pt/Pr = {(4 * π * d)2/ λ2} = (4*π*f*d)2/c2
Where,
Pt = Transmit power
Pr = Receive power
λ = wavelength
d = distance between transmitting and receiving antenna
c = speed of light i.e. 3 x 108
From the equation it implies that transmitted signal attenuates over distance as the signal is being spread over larger and larger area from transmit end towards receive end.
1.b) Shadowing effect
• It is observed in wireless communication. Shadowing is deviation of received power of EM signal from average value.
• It is result of obstacles over the path between transmitter and receiver.
• It depends on geographical position as well as radio frequency of EM (ElectroMagnetic) waves.
2. Small Scale Fading
Small scale fading is concerned with rapid fluctuations of received signal strength over very short distance and short time period.
Based on multipath delay spread there are two types of small scale fading viz. flat fading and frequency selective fading. These multipath fading types depend on propagation environment.
2.a) Flat fading
The wireless channel is said to be flat fading if it has constant gain and linear phase response over a bandwidth which is greater than the bandwidth of the transmitted signal.
In this type of fading all the frequency components of the received signal fluctuate in same proportions simultaneously. It is also known as non-selective fading.
• Signal BW << Channel BW
• Symbol period >> Delay Spread
The effect of flat fading is seen as decrease in SNR. These flat fading channels are known as amplitude varying channels or narrowband channels.
2.b) Frequency Selective fading
It affects different spectral components of a radio signal with different amplitudes. Hence the name selective fading.
• Signal BW > Channel BW
• Symbol period < Delay Spread
Based on doppler spread there are two types of fading viz. fast fading and slow fading. These doppler spread fading types depend on mobile speed i.e. speed of receiver with respect to transmitter.
2.c) Fast fading
The phenomenon of fast fading is represented by rapid fluctuations of signal over small areas (i.e. bandwidth). When the signals arrive from all the directions in the plane, fast fading will be observed for all directions of motion.
Fast fading occurs when channel impulse response changes very rapidly within the symbol duration.
• High doppler spread
• Symbol period > Coherence time
• Signal Variation < Channel variation
This parameters result into frequency dispersion or time selective fading due to doppler spreading. Fast fading is result of reflections of local objects and motion of objects relative to those objects.
In fast fading, receive signal is sum of numerous signals which are reflected from various surfaces. This signal is sum or difference of multiple signals which can be constructive or destructive based on relative phase shift between them. Phase relationships depend on speed of motion, frequency of transmission and relative path lengths.
Fast fading distorts the shape of the baseband pulse. This distortion is linear and creates ISI (Inter Symbol Interference). Adaptive equalization reduces ISI by removing linear distortion induced by channel.