Microwave Waveguides
Generally, if the frequency of a signal or a particular band of signals is high, the bandwidth utilization is high as the signal provides more space for other signals to get accumulated. However, high frequency signals can't travel longer distances without getting attenuated. We have studied that transmission lines help the signals to travel longer distances.
Microwaves propagate through microwave circuits, components and devices, which act as a part of Microwave transmission lines, broadly called as Waveguides.
A hollow metallic tube of uniform cross-section for transmitting electromagnetic waves by successive reflections from the inner walls of the tube is called as a Waveguide.
The following figure shows an example of a waveguide.
A waveguide is generally preferred in microwave communications. Waveguide is a special form of transmission line, which is a hollow metal tube. Unlike a transmission line, a waveguide has no center conductor.
The main characteristics of a Waveguide are −
· The tube wall provides distributed inductance.
· The empty space between the tube walls provide distributed capacitance.
· These are bulky and expensive.
Advantages of Waveguides
Following are few advantages of Waveguides.
· Waveguides are easy to manufacture.
· They can handle very large power (in kilo watts).
· Power loss is very negligible in waveguides.
· They offer very low loss (low value of alpha-attenuation).
· When microwave energy travels through waveguide, it experiences lower losses than a coaxial cable.
Types of Waveguides
There are five types of waveguides.
- Rectangular waveguide
- Circular waveguide
- Elliptical waveguide
- Single-ridged waveguide
- Double-ridged waveguide
The following figures show the types of waveguides.
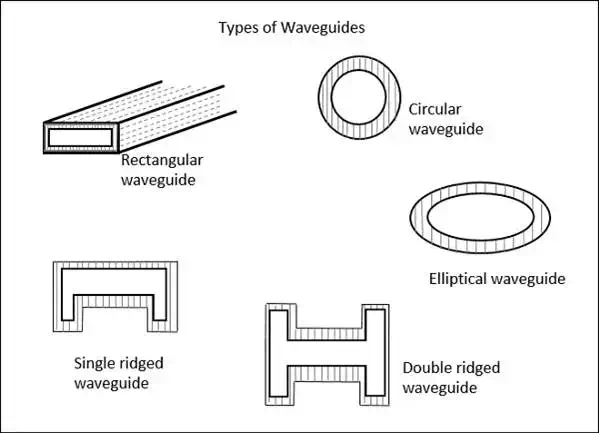
The types of waveguides shown above are hollow in the center and made up of copper walls. These have a thin lining of Au or Ag on the inner surface.