Pulse Amplitude Modulation
Pulse amplitude modulation is defined as the data transmission by altering the amplitudes (power levels or voltage) of every pulse in a regular time sequence of electromagnetic pulses. The possible number of amplitudes can be infinite, but mostly it is some power of two so that the final output signal can be digital. For example, in level-4 PAM there are 22 discrete pulse amplitudes; in level-8 PAM there are 23 discrete pulse amplitudes.
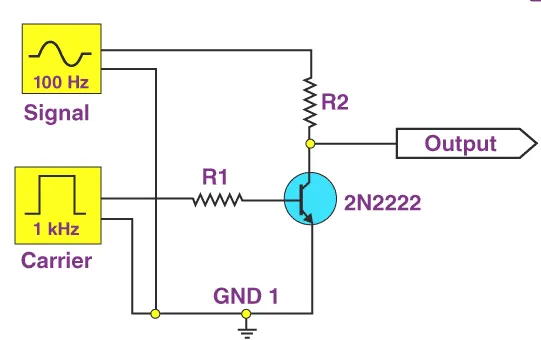
Pulse Amplitude Modulation Circuit
The circuit diagram of PAM looks like :

Pulse Amplitude Modulation Circuit[/caption]
Pulse Amplitude Modulation Block Diagram
The block diagram of PAM looks like:

Pulse Amplitude Modulation Block Diagram[/caption]