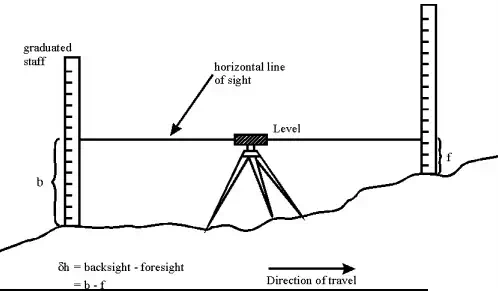
Methods of Levelling
· Method 1 : It is done with only one setting of the instrument.
· Method 2: When the two station points are wide apart and the instrument is set up at more than one point and the levelling is carried out.
Method 1
With only one setting of the instrument:
· The instrument is set up at a point between P and Q and the temporary adjustments carried out.
· The levelling staff is held at P, the elevation of which is known already.
· A back sight is taken on the staff held at P. The staff is then held at Q and the foresight is taken.
Height of the instrument = Known elevation of P + the staff reading at P = 100.00+ 2.10 = 102.10 m
Elevation of Q = Height of the instrument – the staff reading at Q = 102.10 – 1.80 = 100.30 m
Method II
When the station points are wide apart, the instrument is setup for at more than one point and levelling is done (Height of Collimation Method)
· A change point (C.P) is established in between P and Q.
· A back sight is taken at P and a fore sight is taken at the change point.
· The instrument is shifted to another point between the change point and Q.
· A back sight is taken at the change point and a fore sight is taken at Q.
· Any number of change points are established as required.
· This method is known as Height of Collimation method.
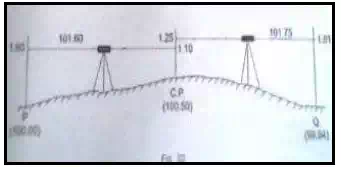
The elevation of change point = Elevation of P + Back sight at P – Fore sight at change point (C.P)
= 100.00+1.60-1.10 = 100.50 m
The second height of the instrument = The elevation of change point+ Back Sight at change point
= 100.50+1.25 = 101.75 m
The elevation of Q = The second height of instrument – foresight at Q
= 101.75 – 1.81 = 99.94 m
Rise and Fall Method of calculating the level:
· The staff readings of the points observed from the same setting of the instrument are compared.
· It is found whether a point is above or below the preceding point.
· If the point is above, the staff reading will be less than the preceding point. The difference between the staff readings is called rise.
· If the point is below the preceding point, the staff reading will be greater than that at the preceding point. The difference between the staff readings is termed fall.
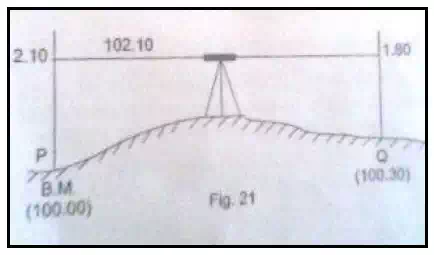
The difference between the staff readings
at P and Q = 2.10 – 1.80 = 0.30 (rise)
Hence, level of Q = Elevation of P + Rise
= 100.00+0.30 = 100.30 m