Intumescent Paint and Coatings
Spray-on fireproof coatings
are an effective method for protecting equipment and structures from fire and
heat. However, these materials tend to have particular advantages and
disadvantages. Read this article to learn about the properties, indications and
applications for these coatings.
An intumescent paint is a type
of coating that is a fire retardant that also protects structural members from
the ill effects of hot weather and sun exposure. It can be applied to wood,
bricks, walls, and other structural members of a structure, to steel and
plastic piping, and to fiberglass structures. These coatings are usually made
of organic substances like epoxy resins and other thermosetting polymers that
have high resistance to heat and fire.
How Intumescent Spray-On Fireproofing Works
Intumescent substances swell
when exposed to heat and fire. When used as a paint coat or fireproofing spray,
they form a protective layer on the surface. When exposed to fire or excessive
heat, the protective layer will resist and absorb heat, thus protecting the
structural member from damaged or deformation. Volume expansion and density
reduction takes place when temperature starts to rise. Organic materials used
for the manufacturing of intumescent paints are inert at low temperatures, but
they swell instantaneously when brought into contact with heat or fire.
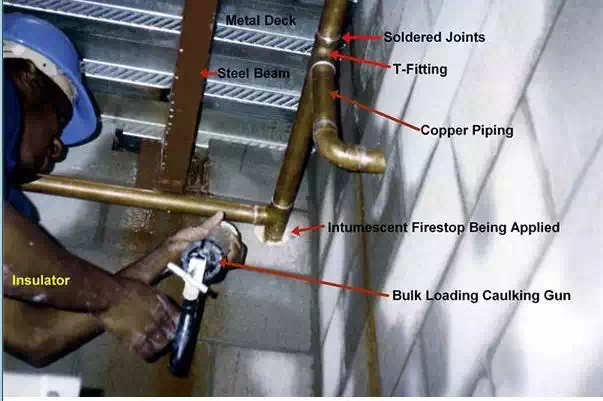
Intumescent paints are either
solvent based or water based. In both cases, they contain a sufficient amount
of hydrates to help in cooling off the temperature because of evaporation
effects. Water based paints are used most often because they are inexpensive
and widely available. Solvent based intumescent paints have, so far, seen only
limited usage.
Another classification system,
which takes into account the nature of the char produced by intumescent paint,
is also in effect.
Soft char intumescent paints produce
only a light char upon initial heat exposure. The char is a bad conductor of
heat, and it does not allow the heat to pass through the paint coat and reach
the structural member. It also contains hydrates which have a cooling effect.
This is used primarily for the protection of structural steel.
Hard char intumescent paints
produce hard char, which is also a very poor conductor of heat. These paints
are exclusively used for plastic pipe protection. The major constituents of
hard char are graphite and sodium silicate.
Advantages and Applications
Intumescent coatings prolong
the structural life of steel. As protected steel is less exposed to frequent
temperature variations, its load bearing capacity also increases.
The coatings can be applied
off-site as well as on-location. Off-site fireproofing means there is enough
time for workers to fit, erect, and adjust their structural components. Faster
and easier construction, reduced on-site activities, and ease of assembly are
the major advantages of off-site coating.
These specialized paints have
a wide range of use. They can be used for steel coatings, wooden coats, or for
structural components like concrete as well. Recently intumescent fireproofing
sprays have been developed that can be applied to fiber glass
structural components, too.
Advantageous use of these
products can be made in refurbishment projects. The structural, aesthetic, and
architectural value of the structural objects remains preserved.
As already stated, intumescent
paints have a huge scope of use. These paints are mainly used in fire-stopping,
closures, and fireproofing works in buildings, houses, and manufacturing
industries. Gasketing applications also
make use of intumescent spray-on fireproofing paints. Major use of these paints
is found in offshore drilling, aircraft maintenance, and the ship building
industries.
Disadvantages
The intumescent fireproofing
industry is on the rise and has already created a stir in the market. However,
there are certain drawbacks associated with these paints.
UV exposure, operational heat,
and the humidity of the work area are three major factors that affect the
performance of intumescents. Intumescents are particularly vulnerable to
environmental exposure at the time of application.
For sodium silicate based
intumescent fire sprays, having rubber or epoxy in the coatings becomes
mandatory in order to promote adherence.
They have a limited fire
resistance period. The best quality, i.e. most expensive, intumescent fire
sprays will not preserve your structural member for more than sixty minutes or
so. As the fire resistance time duration increases, the costs also increases,
and the cost rise is usually exponential.
Alternatives to
the Intumescent spray-on paints are also available in the market.
Flexible blanket
systems - Good - cheap,
easy to use, dry fixing methods; bad - poor appearance.
Other
fireproofing sprays - Good
- covers complex details, low cost, durable; bad - on site application means
more on-site headaches.
Board systems
- Good - clean
appearance, dry fixing, can be used on unpainted steelwork; bad - does not
cover complex areas.