
Gravity Loads
Gravity loads are the vertical forces that act on a structure. The weight of the structure, human occupancy and snow are all types of loads that needs to have a complete load path to the ground.

The simple structure in the above picture can be used to demonstrate how gravity loads move from the top of a structure to the ground.
1. A floor slab is designed to support the imposed gravity load.
2. This load travels from the floor slab to the beams that support it.
3. Upon reaching the beam, the load travels to the end of a beam, which is connected to a girder.
4. This girder is supporting the accumulated loads from the floor slab and beams and transmits the load to a connecting column.
5. The load then travels down the column to the foundation and is distributed to the ground.
Lateral Loads
Gravity loads are not the only type of load that is considered when designing a structure. Lateral loads (wind and earthquake loads) must also have a complete load path to transfer them to the ground. Unlike gravity loads, which act in a downward direction, lateral loads can act in a horizontal direction or even cause an uplift effect.
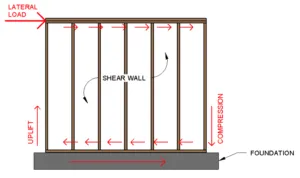
A shear wall is a compilation of smaller structural elements into one larger element that is used to resist lateral loads. The shear wall in the above picture shows how a lateral load moves from the top of the structure to the ground.
1. The lateral load is distributed throughout the top of the wall.
2. This load travels through the shear wall and is output at the base of the wall.
3. The connection between the base of the wall and the foundation forces the load into the foundation and is eventually transferred to the ground.
A complete and continuous load path is necessary to safely move the loads from the top of a structure to the ground. If a correct path isn’t designed to move the load to the ground, then the loads will find other means of making it to the ground; usually in an unfavorable way. It’s not quite as simple as an apple falling on Newton’s head, but it’s essentially the basic law of gravity.
