Strategy implementation: Organizing for action
Strategy implementation is the sum total of the activities and choices required for the execution of strategic plan by which strategies and policies are put into action through the development of programs , budgets and procedures. Although implementation is usually considered after strategy has been formulated, implementation is a key part of strategic management. Thus strategy formulation and strategy implementation are the two sides of same coin.
Implementing strategy
Depending on how the corporation is organized those who implements strategy will probably be a much more divorced group of people than those who formulate it. Most of the people in the organization who are crucial to successful strategy implementation probably had little to do with the development of corporate and even business strategy. Therefore they might be entirely ignorant of vast amount of data and work into formulation process. This is one reason why involving middle managers in the formulation as well as in the implementation of strategy tends to result in better organizational performance.
Developing programs, budgets and procedures
The managers of divisions and functional areas worked with their fellow managers to develop programs, budgets and procedures for implementation of strategy. They also work to achieve synergy among the divisions and functional areas in order to establish and maintain a company‘s distinctive competence.
Programs
A program is a statement of the activities or steps needed to accomplish a single use plan. The purpose of program is to make a strategy action oriented.
Budgets
A budget is a statement of corporation‘s program in monitory terms. After programs are developed, the budget process begins. Planning a budget is the last real check a corporation has on the feasibility of its selected strategy.
Procedures
Procedures are system of sequential steps or techniques that describe in detail how a particular task or job is to be done.
Synergy
One of the goals to be achieved in strategy implementation is synergy between functions and business units. The acquisition or development of additional product lines is often justified on the basis of achieving some advantages of scale in one or more of company‘s functional areas. For example LG developing a product such as DVD Player will help it to achieve synergy by utilizing the same channel.
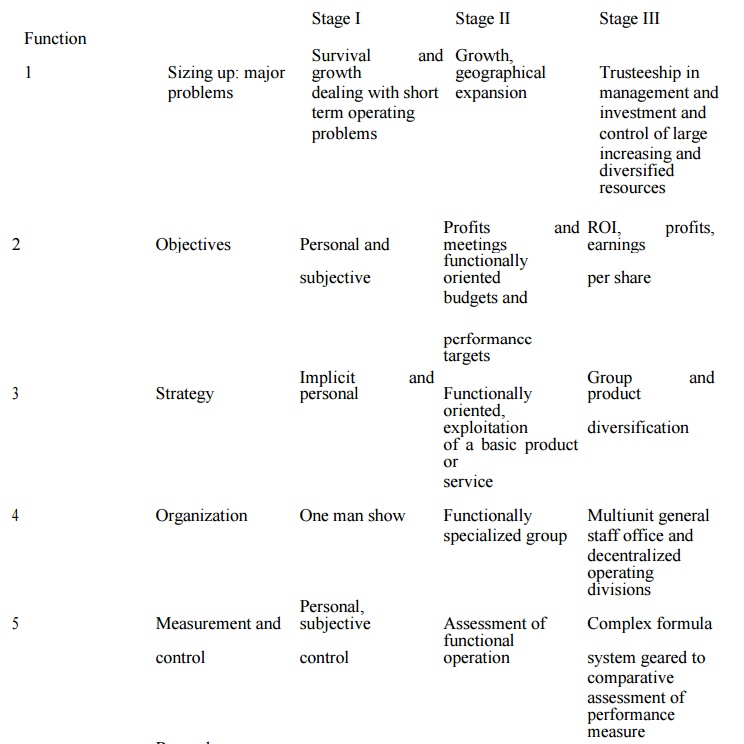
Stages of corporate development
Successful Corporation tend to follow a pattern of structural development called stages of development as they grow and expand. Beginning with the simple structure of the entrepreneurial firm, they usually get larger and organize along functional lines with marketing production and finance department. With continuing success the company adds new product lines in different industries and organizes itself into interconnected divisions. The differences among these three stages of corporate development in terms of typical problems, objectives strategies, reward systems and other characteristics as specified in detail in table.


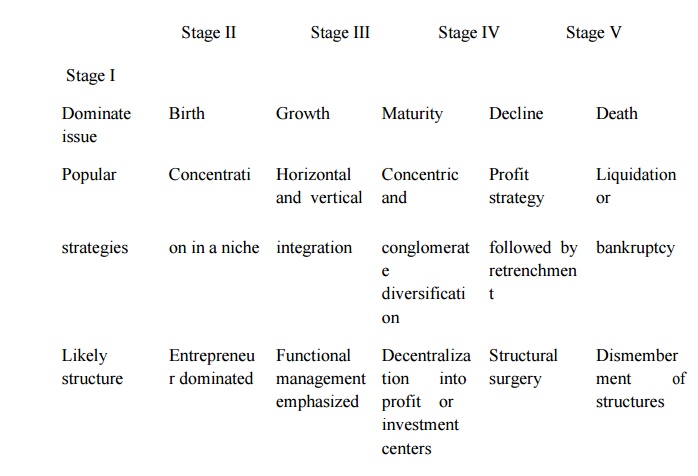
Organizational life cycle
The organizational life cycle describes how the organization grow, develop and eventually decline. The stages of organization life cycles are
1. Birth;
2. Growth;
3. Maturity;
4. Decline;
5. Death
The impact of these stages on corporate and structure are summarized in the table
An organizational structure
The prime purpose of organizational structure is to reduce the external and internal uncertainty. It defines the relationships within the organization and eternal organization. It consists of activities such as task allocation, coordination and supervision, which are directed towards the achievement of organizational aims. It can also be considered as the viewing glass or perspective through which individuals see their organization and its environment.
Many organizations have hierarchical structures, but not all organizations have hierarchical structures. An organization can be structured in many different ways, depending on their objectives. The structure of an organization will determine the modes in which it operates and performs. Organizational structure allows the expressed allocation of responsibilities standard operating procedures and routines rest. Second, it determines which individuals get to participate in which decision-making processes, and thus to what extent their views shape the organization‘s actions.
Operational organizations and informal organizations
Organizational processes are designed to help the organizations to have effective and efficient use of resources. If the informal organizations are formed and try to offset the formal organizations there is likely to be a inefficiency in the organization.