Organizational Life Cycle
Organizational life cycle is the way of describing the organizational development over time.
Like other biological and social organisms, the organization creates, develops and changes. It goes through the growth, crises and eventually dies. There are many ways to describe the organizational development.
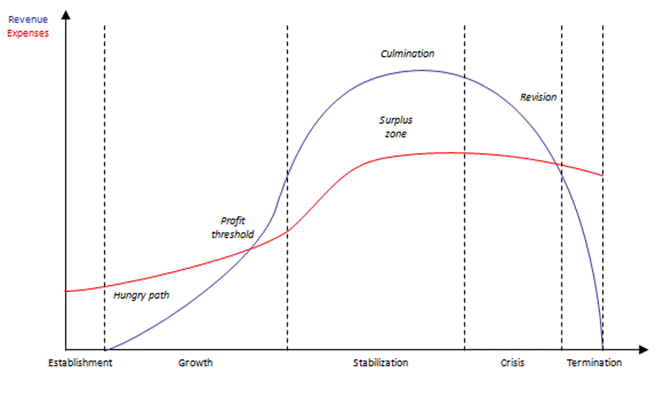
One of the most frequent models is the model of the enterprise lifecycle, which was published by Danny Miller and Peter Friesen. The model describes the mutual development of revenue and expenses during the cycle. The cycle consists of five phases (see figure):
● Establishment - There are only expenses, the company consumes the investment
● Growth - expenses exceed revenues, the company is in loss
● Stabilization - revenues exceed expenses, the company is profitable
● Crisis - incomes fall below the level of expenses, the company gets into loss
● Termination - the company can not handle the crisis, the loss is unbearable, business ends
The model is the result of long study of many businesses, but it is not applied generally. In the life of long-lived enterprises (organizations) different phases take their turn . Many companies have several repeat cycles and even after a long time may not get to the stage of termination, while many companies undergo only one cycle and then it terminates. Long-term maintenance of the organization in a stable phase is the main task of managers at all levels.
Model and its phases are similar to the product life cycle.