The Problem Statement: Is it necessary in Lean Six Sigma?
"If I had 1 hour to save the world, I would spend 55 minutes to find the problem and 5 minutes to think of a solution."
~Einstein
Problem Statement:
A problem statement is a clear description of an area of concern that exists in an organization. It reveals a difficult condition that needs improvement or elimination. It evaluates the gap between the current position and the aspired position of an organization.
Purpose of Problem Statement:
When there is a problem that interferes with the proper flow of work in an organization, such organization calls Business Analysts to formulate a problem statement.
Writing a problem statement should help in careful decision-making for project approval. Often, the problem statement will serve as the basis for the introductory section of a final proposal, directing the reader's attention to the issues that your proposed project will address.
The ultimate goal of a statement of the problem is to transform a generalized problem into one that can be resolved through careful decision-making. More so, it should address a gap in knowledge of the organization, explain the effects and financial implications of the problem.
From the statement of problems, customers and stakeholders should know the problem, what measures and solutions to resolve them. The problem statement is said to be right if it fulfills the above criteria.
Defining the Problem Statement:
A problem should be established before declaring it in the form of a problem statement. Identifying a general problem is not as difficult as determining the actual problem. The human mind tends to start working immediately on a solution once the problem is found. The correct process is to identify the problem, to define the problem in detail, and then to design the solution. The weak definition of the problem is detrimental to solution implementation.
As mentioned, it is a personal job to formulate a problem statement, whereas it's a joint effort to define the problem. If one can comprehend all the actions concerned, a problem can be correctly described. How do they all work? How is it affecting everyone?
Take, for instance, a beverage manufacturing company that makes carbonated water in glass bottles. Due to some reasons, the company management claims that there are at least 50 glass bottle breakages per shift in the plant (three shifts per day), during the filling and sealing process of carbonated water.
The first step is to define the problem. The following questions are to be answered to determine the problem.
- Where does this occur?
- During the whole process, the bottles ruptured when the bottles were filled and sealed.
- When did it happen?
-The rupture occurs randomly without a specific moment.
- How does it work?
-The bottles that are used after filling and when clamped are blasted.
- What is the course?
-The issue must be with the pressure or the temperature since the bottles were blasting.
- Who is causing the problem?
-The problem has to be the quality of the bottle or the sealing machine, causing stress.
- Why does it happen?
-The used bottles cannot resist pressure when the bottles are sealed.
Generally, 5 Whys analysis is the most commonly used tool for finding the exact problem.
Problem statement acts as a driving factor in many projects including Lean Six Sigma Projects. A Lean Six Sigma project involves the following steps:
>Define
>Measure
>Analyze
>Improve
>Control
The five phases of the project are interconnected, following the waterfall model.
The Waterfall model is segmented into different stages of a project. Each phase relies on the results from the earlier process. As mentioned above, the driving force of a project is the problem statement.
Define:

At this stage, the problem is defined. The defined problem is framed in the form of a declaration called the problem statement. Consider the drink manufacturer mentioned earlier. The organization has a problem, and it was cited. Now, let's see how the problem statement looks;
"The company's packing process should aim to reduce bottle disintegration for the process to be smooth and efficient."
Measure:

The next step in action is measuring the current performance or process. At this point, the problem mentioned earlier is quantified by:
· Measuring the ongoing processor performance.
· Identifying the units of measurement.
· Develop the data collection plan.
· Describe the problem based on data collected.
The problem statement made at the "define" stage is the basis for all of these measurements.
"There is a daily average of 150 broken bottles in the plant. The cleaning and replacement costs for a broken bottle are Rs.5.00. The total bottle spending per month is Rs.22,500 and Rs.270,000 per year.”
Analyze:

The problem statement clearly shows that the problem is that the bottles are broken. Thus, in the context of analysis, various techniques and instruments have been used to identify the exact problem which causes the breakage of bottles. The "Analyse" stage is aimed at identifying the problem.
"The problem may be the quality of the bottles, variations in the pressure during the filling and sealing, the shape and quality of the bottle caps, and changes in the process temperature."
Improve:

We now know the cause of the problem and the actual problem. The next step is the "improve" phase. Here, the implementation and verification of the solution occur.
"After all problem factors are determined by the impact they have had in the decreasing order, and solutions have been found to remove them."
Control:

The next is the "control" phase.
The purpose of the six sigma control stage is to verify that the solution implemented at the "improve" phase is adequate; using various tools.
"To keep up the solutions that have been implemented in the "improve" phase and check whether they eliminate or reduce the problem factors."
Lean means waste disposal, on the other hand. A total of seven kinds of waste are categorized using the acronym TIMWOOD.
They are:
T- Transportation
I - Inventory
M- Motion
W- Waiting
O- Over Processing
O- Over Production
D- Defects
In Lean Six Sigma, a problem statement is of great importance when it emphasizes the disposal of waste. If a problem statement is misleading, the whole DMAIC method leads to over-processing and faults. And this makes no meaning for lean six sigma. Therefore, the most crucial thing in the entire project is the problem statement.
In any industry, it is regarded as a project when implementing Six Sigma or Lean Six sigma. There will be a problem in any project; hence, the project must start to find a solution. Implementation of Six Sigma or Lean Six Sigma on its own could be a project. Many factors can be involved in the success or failure of a project. Method, engagement, and interpretation of the problem statement can be the significant factors.
Let us discuss the whole process using a geometric image.
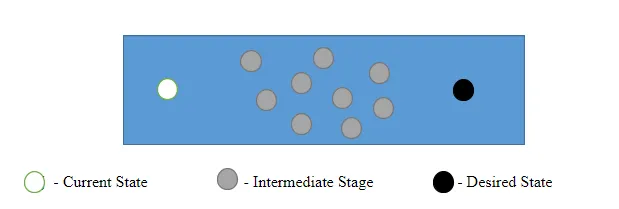
"Current state" means the same as the organization process, "intermediate states" are the solutions available to overcome the existing problem and helping to reach the "desired level."
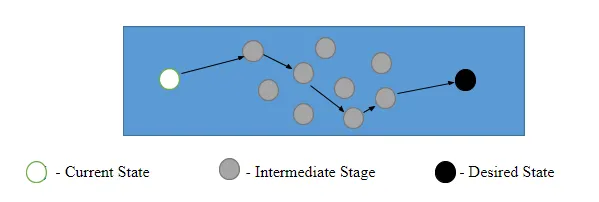
We know that the driving factor in a project is the problem statement, and DMAIC is entirely driven by the problem statement in the define phase. So, if a problem statement is explicitly formulated, this is how the project works and helps to achieve the desired state.
Now, let's see the project flow if the statement of the problem is inappropriate.
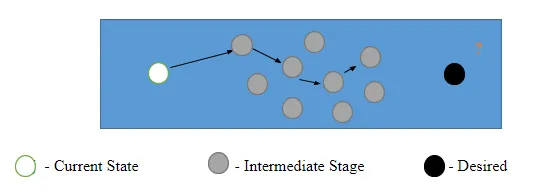
From the figure above, it is evident that we don't know where to go and what to do next. We realize at that point that the total efforts are a waste and should restart the process, leading to a waste of effort, time, and over-processing. Therefore for a project to be completed in due course and meeting the requirements, the problem statement has to be appropriate.
How to identify a problem statement
· It should neither be a statement of the Vision and Mission of the company nor any philosophy.
· A problem statement should be brief and clear.
· A problem statement should be specific and measurable.
· The context must always be made clear.