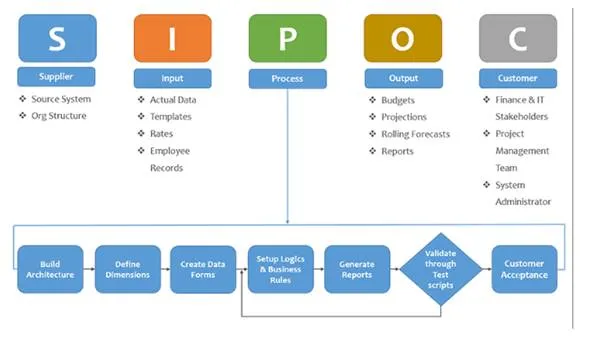
Type 1 Process Map: SIPOC Map
The Level 1 process map, we see the overall process, these process maps are mostly used at the Define phase, where, we need to have a hawk eye view of the overall process. The whole process, with their inputs, suppliers, outputs, and customers with few process steps.
In the mapping hierarchy, the highest order tool is SIPOC. It gives the information which is Critical to Business, Critical to Quality and the critical to customers. And by this, we get a better understanding of all components.
Nowadays SIPOC is called SIPOC-R, where R represents Requirement.

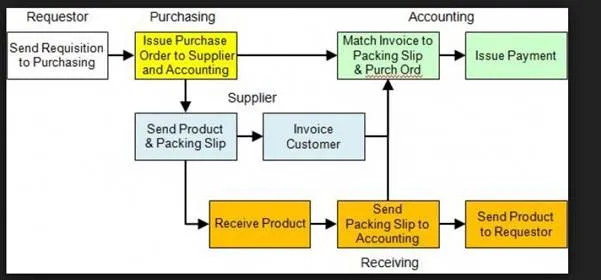
Type 2 Process Map: Deployment Map
These types of process maps are used for the stakeholders. It gives the information of how the process works. Stakeholders are neither interested nor do they have any requirement to know the detailed process steps; however, the major process steps would be covered in these maps.
These maps would do not need to contain the whole process knowledge; therefore, it can be prepared with the help of process manager. This is a more elaborative SIPOC, where we get some more process information. There would be more process steps.
This is also a deployment process map, where we can see the connection and dependencies on other processors. In Visio, we can use the deployment with the signal or could use the different colors in normal process maps so that the other processes should be highlighted.
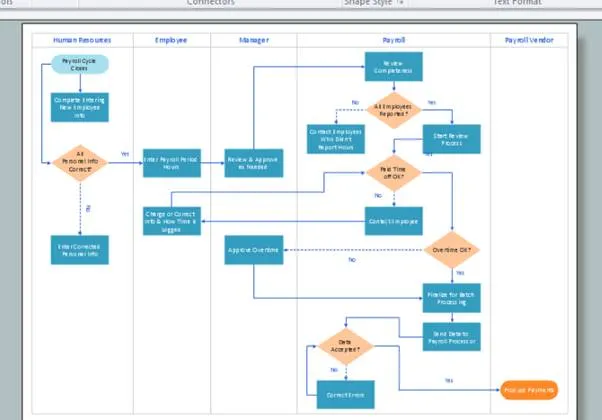
Type 3 Process Map: Swimlane Map
The Level 3 process maps are those maps, which have detailed info of the process, it is the micro level process maps. It gives the whole process steps at once if a new processor can understand how to do the task at once. We generally do not much need of seeing the whole process, however, some part of the process must be needed to see at once. The detailed process maps would work in that case.
This is also called the Swimlane map, it also has layers and sequence wise representation of the process. Here we can figure it out, who does what. However, it has a drawback, due to being a detailed map, it is very huge and it is very space efficient.
To see the whole process at once take more time. And understand the process is also a bit difficult, only the expertise could understand.
These types of process maps, we use to see the gaps, issues or unnecessary steps to resolve the issue or could work and decrease the lead time/cycle time. By cut shorting the process steps could help us to decrease the number of employees.
Even sometimes the whole micro-level process map shows, in which area we need to more focus. We can find the pain area, could start the treatment of that particular while seeing that area as a whole.
Value Stream Mapping
Value Stream Map is used to understand what is valuable to the process and what is non-value added. The VSM is also called the Material and Info flow map. Greater amount of skill is required for making the VSM, however, it consists of excessive info.
The Value Stream has all the actions which bring the main flows and give the service to the customers. Usually, every process has 3 types of conditions, first - What you have thought about the process? What actually the process is and how the process should be? How the process should remove the unnecessary steps while seeing the NVA in the VSM process maps?
The VSM is used in the Lean concept, it is the tool of Lean, it shows the Pull scheduling or opportunity to do the pull scheduling. It is used when we plan for process improvement. VSM is often used when planning a Lean implementation to display the current state of the process including material, information flows and any other information important for Lean implementations.
Here let’s discuss in brief what is Value Add and what is Non-Value Add?
1. Value – Capabilities of the product or process as defined by the customer, provided in the right form, at the right time and for the suitable cost.
2. Value Added and Nonvalue Added – In simple words, if the customer is willing to pay for something, it is the value-added service and if the customer is not willing to pay or there are unnecessary steps then it is counted as Non-Value-added services.
There are chances that customer would not be willing to pay, however as per the internal control those steps are required, such NVAs are called NVAR.
