INDIAN SPACE PROGRAMME
The Indian space program began in 1962. In 1969 the Indian space Research Organization (ISRO) was set up and headquartered in Bangalore (presently Bengaluru) for the purpose of rapid development of space technology and its application. In 1972, space commission was established. In 1975, India launched its first satellite, Aryabhata, and thus entered the space age. Over the last four and half decades, the Indian space programme has made impressive progress through a well integrated, self-reliant programme.
The Indian space program began in 1962. In 1969 the Indian space Research Organization (ISRO) was set up and headquartered in Bangalore (presently Bengaluru) for the purpose of rapid development of space technology and its application. In 1972, space commission was established. In 1975, India launched its first satellite, Aryabhata, and thus entered the space age. Over the last four and half decades, the Indian space programme has made impressive progress through a well integrated, self:reliant programme.
Indian Space Research Organization
Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO), set up at Ahmadabad in 1969 by Prof. Vikram Sarabhai as chairman, is the apex body to provide guidelines, formulate policies and monitor implementation of the national space policy.
Objectives of ISRO
Directed towards, self reliant use of space technology for national development with the main thrust on:
I. Mass communication and education via satellite.
II. Survey and management of natural resources through remote sensing technology, environmental monitoring and meteorological forecasting.
III. Development of indigenous satellites and satellite launch vehicles.
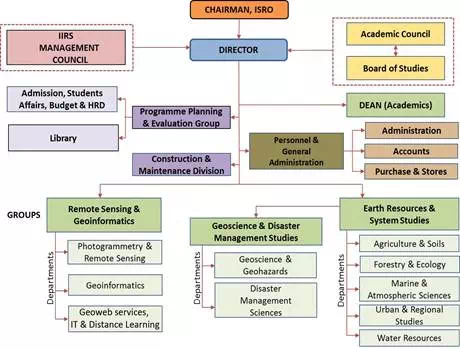
Organizational Structure of the ISRO
Other Space Research Organizations
I. Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC): VSSC at Thiruvananhapuram is the head centre for the development of satellite launch vehicles and associated technology.
II. ISRO Satellite Centre (ISAC): ISAC at Bangalore is the lead center for developing satellite technology and implementation of satellite system for scientific technological and applications missions.
III. Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC) SHAR: SDSC SHAR is the main launch centre of ISRO and has facilities for solid propellant casting, static testing of solid motors, launch vehicles integration and launch operations, range operation comprising telemetry tracking and command network and mission control centre.
IV. Liquid Propulsion System Centre (LPSC): LPSC is the lead centre in development of liquid and cryogenic propulsion for launch vehicles and satellites.
V. Space Applications Centre (SAC): SAC at Ahmadabad is engaged in the development of pay loads for communication, meteorological and remote sensing satellites.
VI. Development and Educational Communication: Unit (DECU): DECU at Ahmadabad is involved in the conception, definition, planning, implementation and socio:economic evaluation of innovative configuration for space applications.
Chandrayan I: India's First Lunar Probe
VII. VII ISRO Telemetry, Tracking and Command: Network (ISTRAC): ISTRAC provides mission support to low:earth orbit satellites as well as launch vehicle missions.
VIII. Master Control Facility: MCF at Hassan in Karnataka and Bhopal in Madhya Pradesh monitors and controls all the geo:stationary satellites of ISRO.
IX. ISRO inertial system Unit (IISU): IISU at Thiruvanathpuram carries out resource and development in inertial sensors and systems.
X. National Remote Sensing Agency (NRSA) : NRSA at Hyderabad is an autonomous institution under DOS. The agency is responsible for satellite data acquisition and processing data dissemination, aerial remote sensing and decision support for disaster management.
XI. Physical Research Laboratory (PRL): PRL at Ahmadabad, is an autonomous institution supported mainly by DOS. It is premier institute for multi:disciplinary research in astronomy and astrophysics, earth sciences, planetary sciences, space sciences and basic science.
Types of Satellites Launched by ISRO
XII. National Atmospheric Research Laboratory (NARL): NARL at Gadanki near Tirupati is an autonomous society supported by DOS. It is a premier centre for atmospheric research facilities like Mesosphere, Stratosphere troposphere radar, LIDAR etc.
XIII. Regional Remote Sensing Service Centres – (PRSSC) – Five PRSSCs have been established by the DOS at Bangalore, Jodhpur, Kharagpur, Dehradun and Nagpur. PRSSCs support the various remote sensing tasks specific to their regions as well as at the national level.
XIV. North Eastern – Space Application Centre (NE SAC): NE-SAC, located at Shillong, is a joint initiatives of DOS and North Eastern Council to provide development support to the North Eastern region using space science and technology.
XV. Antrix Corporation Limited – The Antrix Corporation Limited, Bangalore is the apex marketing agency under DOS with access to resources of DOS as well as Indian space industries.
XVI. Semi:Conductor Laboratory (SCL): SCL is entrusted with design and development of very large scale integration ( VLSI) devices and development of systems for telecommunications and space sectors.