Power supply subsystem
Power Subsystem The power system is necessary for the other CubeSat subsystems, such as the microcontroller and communication, to function. The design objectives of the power system include: providing sufficient power to the electrical subsystem, minimizing power drain from the batteries, ensuring efficient recharging of the batteries, and minimizing weight and volume. In addition, Satellite Solutions hopes to improve upon Sub-OrbitalTechnologies’ power system.
The preliminary design of Satellite Solutions’ CubeSat power system implemented various power generation methods, a DC-to-DC boost converter, a battery charger, rechargeable batteries, and a DC-to-DC converter. Parts for that power system have been ordered; however, due to a back order of 8-14 weeks, a redesign of the system was necessary to provide parts faster. As a result, the power system has multiple design options due to different component specifications. Some of the design options change battery configuration (series or parallel) and the method of power delivery to the CubeSat subsystems. The redesign of the system also resulted in a new design strategy that examined the power system from the load to the source. The strategy is based on the idea that each component is dependent upon the component from which it receives power.
The following discussion presents a final design review of the power system by Satellite Solutions. First, the general operation and problems of the CanSat power system are given. Next, the CubeSat power system is divided into three main areas, which include: power generation, storage, and distribution. A general layout of the power system is presented in Figure 18, which provides a road map for discussing the areas of interest. Note that the power distribution and generation elements are explained first in order to define the requirements of the power storage element Figure 18: General Layout of the CubeSat Power System

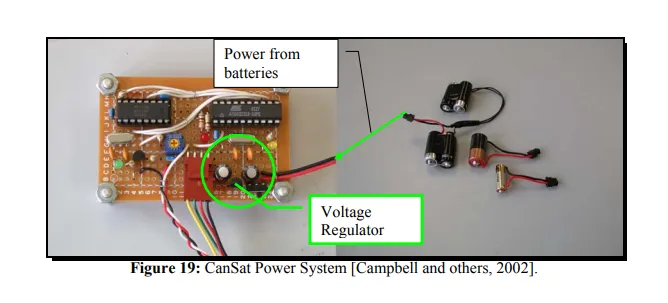
Within each area, the component design, requirements, evaluation criteria, and best option(s) for a particular design are presented. The review of the power system provides general information about the components, but is mostly concerned with component evaluation. Last of all, final design options are presented based on the power system energy balance, cost, and future adaptability. A basic understanding of circuit theory is expected and assumed known for the following explanations. 5.1 Background The CanSat power system is composed of two independent battery sources, a voltage regulator, and two capacitors, as seen in Figure 19. Despite its simplicity, the CanSat power system had some shortcomings: the dual battery sources added unnecessary weight, the batteries had to be replaced frequently, and the voltage regulator was incorrectly matched to the power supply (voltage drop out was too high).
Background
The CanSat power system is composed of two independent battery sources, a voltage regulator, and two capacitors, as seen in Figure 19. Despite its simplicity, the CanSat power system had some shortcomings: the dual battery sources added unnecessary weight, the batteries had to be replaced frequently, and the voltage regulator was incorrectly matched to the power supply (voltage drop out was too high).