TRANSMISSION OF HEAT
1) conduction
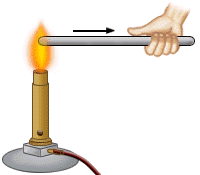
the heat travels through the molecule of substance without movement of molecule themselves.(molecule doesn't travel.)
2) convection :
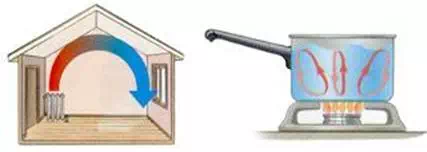
when the fluid (liquid and gas) heated the expands so the heated molecules become lighter and moves upward and cold molecules takes place . this process continues.
3) radiation:
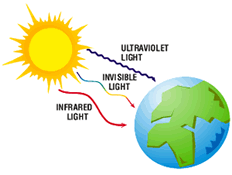
In this way heat travels without any medium. it does not heat the medium approximately. heat travels in a straight line.
e g: heat from sun comes without any medium (zero atmosphere) to the earth by radiation.
FLASH POINT, FIRE POINT, IGNITION TEMP.
FLASH POINT:
The min temp at which the rate of vaporization of fuel is sufficient to produce a momentary flash upon the application of source of ignition.
FIRE POINT:
The min temp at which the burning vapor is capable to enable combustion to continue.
IGNITION TEMP:
The min temp at which fuel will ignite without help of ignition source. it also called "auto ignition temp"
a) spark:
* friction
* static charge
* loose electric connection
* lightening
* welding
b) flame
* match stick
* gas cutting torch
c) heat of chemical reaction
*exothermic reaction
d) heat of compression
e) nuclear heat