Industrial Manipulators And Its Kinematics
Introduction
In this section I will try to give an idea about types of links and joints and the serial chains combination, also to focus on explaining the term (degree of freedom) in an open chain and a closed chain and how to calculate it. Beside that I give several drawing examples about different types of links and chains to make the idea easy and clear to understand. In the end of this section I will define the work space area for a robot and what type of work space we have. I explain 2R and 3R manipulator work space beside the direct and inverse kinematics work space.
First we need to define the following:
Serial chain is a combination of links and joints in the space. Notice: we need to understand the word degree of freedom and to know how to define how many degrees of freedom a robot has.
Links and joints
Joints:
Two different types of joints:
1. Revolute joints(R): this joint is powered by a servo motor.
Revolute joint
Example a robot has three revolute joints, so we call it (RRR) or (3R), which mean three degree of freedom with so called planar manipulator.
Notice: we begin to calculate (R) beginning from base to end effector.
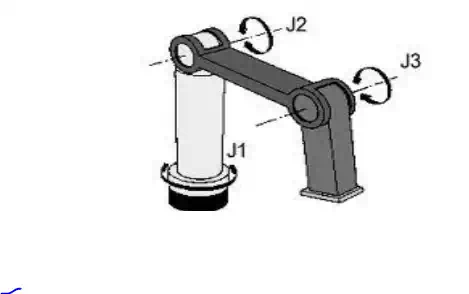
Example of robot with 3 revolute joints
2. Prismatic joints (P): is powered by a cylindrical piston like pneumatic system or hydraulic
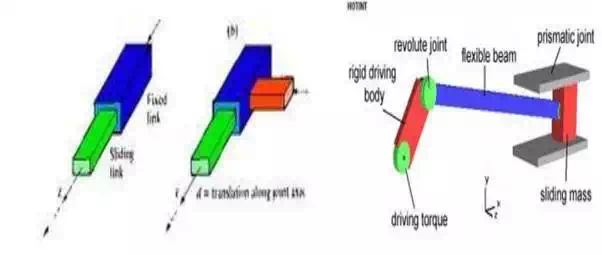
3 Example of prismatic joints
Example of one prismatic and two revolute joints: we call it (RPR) with three degrees of freedom and this model can be called redundant.

Planar RPR
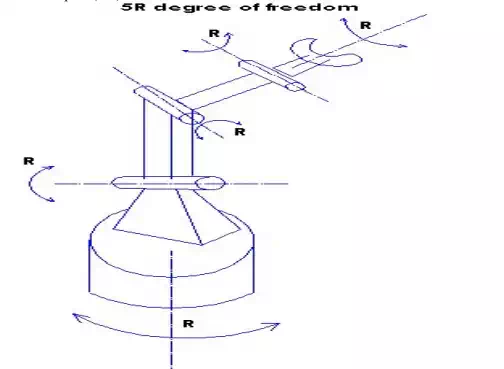
Example of a robot with five degrees of freedom
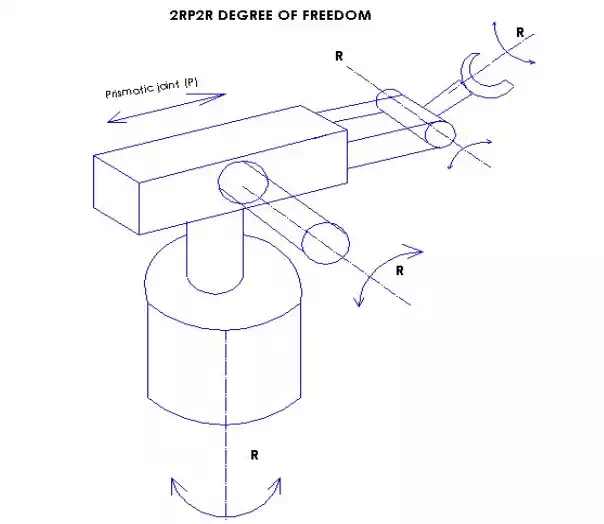
Example of a robot with 2RP2R
In this example we calculate from the base first revolute joint as R then second revolute joint as R. After that comes one prismatic joint so we have so far 2RP, then we end up with 2 revolute joint, then the total will be 2RP2R.
Degree of freedom
First I need to explain the term degree of freedom (DOF). When I fix a joint and prevent any movement then I can say that this joint has zero degree of freedom but when I mount a joint with a motor drive, then it loses two degrees of freedom and it will have just one degree of freedom because it moves in one plane.
Notice: in the space there is six degrees of freedom.
Spherical joints have three degrees of freedom and it moves in three planes.

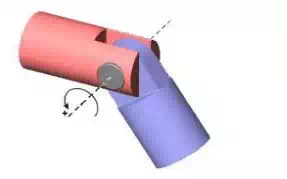
Hooke joint has two degrees of freedom and it move in two planes.
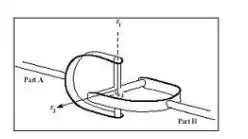
Hooke joint