Management by Objectives
Introduction
There are various management philosophies and types used in the world of business. These types of management differ from one another.
In some cases, a few of these management types can be mixed together in order to create something customed for a specific requirement.
Management by Objectives (MBO) is one of the frequently used management types. The popularity and the proven results are the main reasons behind everyone adopting this technique for their organization.
As valid as it is for many management types, MBO is a systematic and organized approach that emphasizes the achievement of goals. In the long run, this allows the management to change the organization's mindset to become more result oriented.
The Concepts
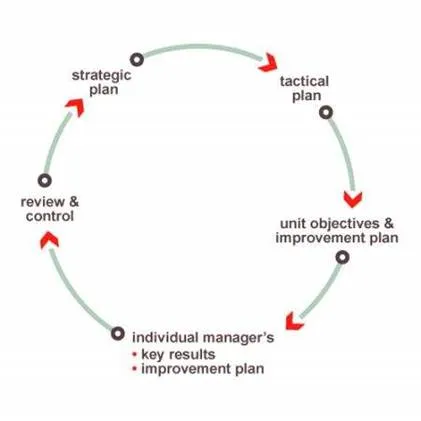
The core aim of management by objectives is the alignment of company goals and subordinate objectives properly, so everyone in the organization works towards achieving the same organizational goal. In order to identify the organizational goals, the upper management usually follows techniques such as GQM (Goal, Questions and Metrics).
In order to set the objectives for the employees, the following steps are followed:
· The management chunks down the organizational goals and assign chunks to senior managers.
· Senior managers then derive objectives for them to achieve the assigned organizational goals. This is where senior managers assign the objectives to the operational management.
· Operational management then chunks down their objectives and identify the activities required for achieving the objectives. These sub-objectives and activities are then assigned to rest of the staff.
· When objectives and activities are assigned, the management gives strong inputs to clearly identify the objectives, time frame for completion, and tracking options.
· Each objective is properly tracked and the management gives periodic feedback to the objective owner.
· In most occasions, the organization defines processes and procedures in order to track the objectives and feedback.
· At the end of the agreed period (usually an year), the objective achievement is reviewed and an appraisal is performed. Usually, the outcomes of this assessment are used to determine the salary increments for year ahead and relevant bonuses to employees.
Activity trap is one of the issues that prevent the success of MBO process. This happens when employees are more focused on daily activities rather than the long-term objectives. Overloaded activities are a result of vicious cycles and this cycle should be broken through proper planning.

The Focus
In MBO, the management focus is on the result, not the activity. The tasks are delegated through negotiations and there is no fixed roadmap for the implementation. The implementation is done dynamically and to suit the situation.
When to use MBO?
Although MBO is extremely result oriented, not all enterprises can benefit from MBO implementations. The MBO is most suitable for knowledge-based enterprises where the staff is quite competent of what they do.
Specially, if the management is planning to implement a self-leadership culture among the employees, MBO is the best way to initiate that process.
Responsibility of Individuals
Since individuals are empowered to carry out stretched tasks and responsibilities under MBO, individual responsibilities play a vital role for the success of MBO.
In MBO, there is a link built between the strategic thinking of the upper management and the operational execution of the lower levels of the hierarchy.
The responsibility of achieving the objectives is passed from the organization to each individual of the organization.
Management by objectives is mainly achieved through self-control. Nowadays, especially in knowledge-based organizations, the employees are self-managers, who are able to make their own decisions. In such organizations, the management should ask three basic questions from its employees.
· What should be your responsibilities?
· What information is required by you from the management and the peers?
· What information should you provide the management and peers in return?
Conclusion
Management by objectives has become de facto practice for management in knowledge-based organizations such as software development companies. The employees are given sufficient responsibility and authority to achieve their individual objectives.
Accomplishment of individual objectives eventually contributes to achieving organizational goals. Therefore, there should be a strong and robust process of assessing the objective achievements of each individual.
This review process should take place periodically and sufficient feedback will make sure that the individual objectives are in par with the organizational goals.