Wind Turbine
Generator Design
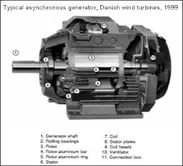
For large, commercial size horizontal-axis wind turbines, the
generator is mounted in a nacelle at the top of a tower, behind the hub of the
turbine rotor. Typically wind turbines generate electricity through
asynchronous machines that are directly connected with the electricity grid.
Usually the rotational speed of the wind turbine is slower than the equivalent
rotation speed of the electrical network - typical rotation speeds for a wind
generators are 5-20 rpm while a directly connected machine will have an electrical
speed between 750-3600 rpm. Therefore, a gearbox is inserted between the rotor
hub and the generator. This also reduces the generator cost and weight.
Commercial size generators have a rotor carrying a field
winding so that a rotating magnetic field is produced inside a set of windings
called the stator. While the rotating field winding consumes a fraction of a
percent of the generator output, adjustment of the field current allows good
control over the generator output voltage. Enercon has produced gearless wind
turbines with separately excited generators for many years, and Siemens
produces a gearless "inverted generator" 3MW model while developing a
6MW model.This gives better reliability and performance than gear based systems.
Older style wind generators
rotate at a constant speed, to match power line frequency, which allowed the
use of less costly induction generators. Newer wind turbines often turn at
whatever speed generates electricity most efficiently. This can be solved using
multiple technologies such as doubly fed induction generators or full-effect
converters where the variable frequency current produced is converted to DC and
then back to AC, matching the line frequency and voltage. Although such
alternatives require costly equipment and cause power loss, the turbine can
capture a significantly larger fraction of the wind energy. In some cases,
especially when turbines are sited offshore, the DC energy will be transmitted
from the turbine to a central (onshore) inverter for connection to the grid.