Introduction To Various Sources Of Energy
There are mainly two types of sources of energy
1. Conventional Sources of Energy (Non-Renewable Sources of
Energy)
2. Non-conventional Sources of Energy (Renewable Sources of
Energy).
Conventional Sources Of Energy
These resources are finite and exhaustible. Once consumed,
these sources cannot be replaced by others. Examples include coal, timber,
petroleum, lignite, natural gas, fossil fuels, nuclear fuels etc. The examples
are
(i) fossil fuel
(ii) nuclear energy
(iii) hydro energy
Have you not seen the filling of fuel in automobiles? What
are the fuels that are being used in automobiles? What type of sources of
energy are they? Are they non-conventional? Fossil fuel is an invaluable source
of energy produced due to chemical changes taking place in the absence of
oxygen, in plants and animals that have been buried deep in the earth’s crust
for many million years. Fossil fuels like coal, petroleum and natural gas are
formed in this manner. These are conventional sources of energy. For example,
energy from, Petroleum, natural gas, coal, nuclear energy, etc
Thermal Power
Thermal generation accounts for about 70% of power
generation in India. Thermal energy generation is based on coal, furnace oil and
natural gas. Steam cycle, rankin cycle or sterling cycle can be used for energy
production. Now clean coal technologies (with 10% ash content) have been used
in thermal power plants on commercial scale.
National Thermal Power Corporation (Ntpc)
It was incorporated in November 1975 as a public sector
undertaking with the main objectives of planning, promoting and organising
integrated development of thermal power. Installed capacity of NTPC projects
stands at 16000 MW.
Non-Conventional Sources Of Energy
These sources are being continuously produced in nature and
are not exhaustible. Examples include wood, geothermal energy, wind energy,
tidal energy, nuclear fusion, gobar gas, biomass, solar energy etc. The
examples are
(i) Solar energy
(ii) wind energy
(iii) geothermal energy
(iv) ocean energy such as tidal energy, wave energy
(v) biomass energy such as gobar gas.
It is evident that all energy resources based on fossil
fuels has limitations in availability and will soon exhaust. Hence the long term
option for energy supply lies only with non-conventional energy sources. These
resources are in exhaustible for the next hundreds of thousands of years.
The sources which are perennial and give energy
continuously and which do not deplete with use are the Non-conventional sources
of energy.
For example, energy from, solar energy, bio-energy, wind
energy, geothermal energy, wave, tidal and OTEC.
Renewable energy development programme Introduction To Various Non Conventional
(Renewable) Sources Of Energy
is gaining momentum in India. It has emerged as a viable
option to achieve the goal of sustainable development. However, Indian
renewable energy programme need more thrust at this stage. India has now the
world’s largest programme for deployment of renewable energy products and
systems, the spread of various renewable energy technologies in the country has
been supported by a variety of incentives and policy measures.
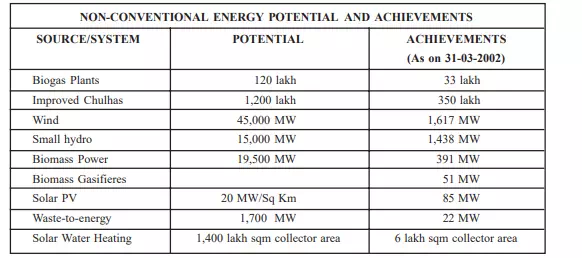
Power generation from non-conventional renewable sources has assumed
significance in the context of environmental hazards posed by the excessive use
of conventional fossil fuels. Renewable energy technologies have provied viable
for power generation not so much as a substitute, but as supplement to
conventional power generation. Currently renewables contribute over 3500 MW,
which represents almost 3.5 percent of the total installed generating capacity
of one lakh MW from all sources. Of this, wind power alone accounts for 1617
MW, while biomass power accounts for 450 MW and small hydros 1438 MW. An
additional 4000 MW of power from renewable sources is to be added during the
Tenth Five Year Plan period (2002–07) mainly through wind, biomass, small
hydros, waste energy and solar energy system. Further, India has set a goal
elevating the share of renewable energy sources in power generation up to 10
percent share of new capacity addition or 10,000 MW to come from renewables by
2012.
Today, India has the largest decentralised solar energy
programme, the second largest biogas and improved stove programmes and the
fifth largest wind energy programme in the world. A substantial manufacturing
base has been created in a variety of renewable energy technologies placing
India in a positron not only to export technologies; but also offer technical
expertise to other countries.