Reaction turbine
Description of reaction turbine
It consists of a wheel or rotor, casing,
fixed and moving blades. In this type, equal number of fixed and moving blades
are attached alternately to the casing and the wheel respectively. The fixed
blades is similar to a nozzle where velocity increases with decrease of
pressure.
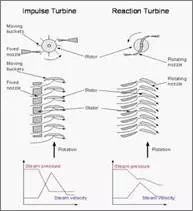
Working Principle
In reaction turbine, the steam is not
expanded in the nozzle, but expands as it flows over the blades.
The steam passes over the fixed blade F.
The fixed Blade changes the direction of steam and at the same time allows it
expand to a higher velocity, with decrease of pressure.
Then the steam passes over the moving blade
M. The moving blade converts the kinetic energy into mechanical work with
decrease of velocity; but at the same time steam expands as it flows over the
moving blade and there is a fall of pressure. This produces a reaction on the
blades, by the expanding steam.
Thus in the reaction turbine the steam
expands both in fixed and moving blades continuously as the steam passes over
them. Therefore, the pressure drop occurs gradually and continuously over both
fixed and moving blades. Parson turbine is an example of reaction turbine.