Diesel power plant
Applications of diesel power plant
1. Diesel power plantís is in the range of 2 to 50 MW
capacity. They are used as central station for small or medium power supplies.
2. They can be used as stand-by plants to hydro-electric
power plants and steam power plants for emergency services.
3. They can be used as peak load plants in combinations
with thermal or hydro-plants.
4. They are quite suitable for mobile power generation
and are widely used in transportation systems such as automobiles, railways,
air planes and ships.
5. Now-a-days power cut has become a regular feature for
industries. The only solution to tide over this difficulty is to install diesel
generating sets.
Layout diesel engine power plant:
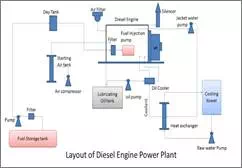
Diesel engine:
Diesel engines or compression ignition
engines as they are called are generally classified as two stroke engine and
four stroke engines. In diesel engine, air admitted into the cylinder is
compressed, the compression ratio being 12 to 20. At the end of compression
stroke, fuel is injected. It burns and the burning gases expand and do work on
the position. The engine is directly coupled to the generator. The gases are
then exhausted from the cylinder to atmosphere.
Engine strating system:
This includes air compressor and starting
air tank. The function of this system is to start the engine from cold
supplying compressed air.
Fuel system:
Pump draws diesel from storage tank and
supplies it to the small day tank through the filter. Day tank supplies the
daily fuel need of engine. The day tan is usually placed high so that diesel
flows to engine under gravity.
Diesel is again filtered before being
injected into the engine by the fuel injection pump. The fuel is supplied to
the engine according to the load on the plant.
Air intake system:
Air filters are used to remove dust from
the incoming air. Air filters may be dry type, which is made up of felt, wool
or cloth. In oil bath type filters, the sir is swept over a bath of oil so that
dust particles get coated.
Exhaust system:
In the exhaust system, silencer (muffler)
is provide to reduce the noise.
Engine cooling system:
The temperature of burning gases in the
engine cylinder is the order of 1500 to 2000íC. to keep
the temperature at the reasonable level, water is circulated inside the engine
in water jackets which are passage around the cylinder, piston, combustion
chamber etc. hot water leaving the jacket is sent to heat exchanger. Raw water
is made to flow through the heat exchanger, where it takes up the heat of
jacket water. It is then cooled in the cooling tower and recirculates again.
Engine lubrication system:
It includes lubricating oil tank, oil pump
and cooler. Lubrication is essential to reduce friction and wear of engine
parts such as cylinder walls and piston.
Lubricating oil which gets heated due to
friction of moving parts is cooled before recirculation. The cooling water used
in the engine is used for cooling the lubricant also.
Advantages of diesel power plant:
1. Plant layout is simple. Hence it can be quickly
installed and commissioned, while the erection and starting of a steam power
plant or hydro-plant takes a fairly long time.
2. Quick starting and easy pick-up of loads are possible
in a very short time.
3. Location of the plant is near the load center.
4. The load operation is easy and requires minimum labors.
5. Efficiency at part loads does not fall so much as that
of a steam plant.
6. Fuel handling is easier and no problem of ash disposal
exists.
7. The plant is smaller in size than steam power plant
for same capacity.
8. Diesel plants operate at high overall efficiency than
steam.
Disadvantages of diesel power plant:
1. Plant capacity is limited to about 50 MW of power.
2. Diesel fuel is much more expensive than coal.
3. The maintenance and lubrication costs are high.
4. Diesel engines are not guaranteed for operation under
continuous, while steam can work under 25% of overload continuously.