Simple vertical boiler
The image shows the simplest form of an
internally fired vertical fire-tube boiler. It does not require heavy
foundation and requires very small floor area.
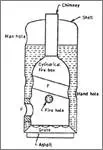
Cylindrical shell:
The shell is vertical and it attached to
the bottom of the furnace. Greater portion of the shell is full of water which
surrounds the furnace also. Remaining portion is steam space. The shell may be
of about 1.25 metres diameter and 2.0 meters height.
Cross-tubes:
One or more cross tubes are either riveted
or flanged to the furnace to increase the heating surface and to improve the
water circulation.
Furnace (or fire box):
Combustion of coal takes place in the
furnace (fire box).
Grate:
It is placed at the bottom of fire box and
coal is fed on it for burning.
Fire door:
Coal is fed to the grate through the fire
door.
Chimney (or stack):
The chimney (stack) passes from the top of
the firebox through the top of the shell.
Manhole:
It is provided on the top of the shell to
enable a man to enter into it and inspect and repair the boiler from inside it.
It is also, meant for cleaning the interior of the boiler shell and exterior of
thecompbustion chamber and stack (chimney).
Hand holes:
These are provided in the shell opposite to
the ends of each cross tube for cleaning the cross tube.
Ashipt:
It is provide for collecting the ash
deposit, which can be removed away at intervals.
Working:
The fuel (coal) is fed into the grate
through the fire hole and is burnt. The ashpit placed
below the grate collect the ashes of the burning fuel.
The combustion gas flows from the furnace,
passes around the cross tubes and escapes to the atmosphere through the chimney.
Water goes by natural circulation due to
convection currents, from the lower end of the cross tube and comes out from
the higher end.
The working pressure of the simple vertical
boiler does not exceed 70 N/cm^2.
The
following mountings are fitted in the boiler:
Pressure gauge: it indicates the pressure of the steam inside
the boiler.
Water gauge (water level
indicator): this indicates the
water level in the boiler.
Safety valve: it prevents an increase of steam pressure intheboiler above its design pressure.
Steam stop valve: it
regulates the flow of steam supply to requirements.