Design Of Heating Surfaces
The first step in the design of heating surfaces is determining the heat duties
of different components of the boiler heating surfaces. Atypical boiler would
use the following four types of heating surfaces:
Economizer
Evaporator
Superheater
Reheater (for reheat boilers)
Heat duty of these elements depends on the designed steam parameter of the
boiler. It is best illustrated by an example (Figure 1), which shows how the
relative heat duty of different boiler elements changes with steam pressure. As
the steam pressure increases, the heat duty of the evaporator decreases and
that of superheater increases.
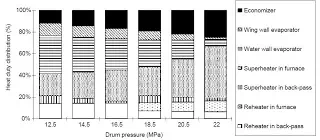
Figure 1
At low pressure the evaporator duty is so high that a water wall or wing wall
alone cannot absorb the required amount of heat. So, a separate heating
surface, called bank tubes, is needed. After the heat duties of individual
elements (economizer, evaporator, superheater, and reheater) are determined by
the steam table, their disposition can be determined. From the viewpoint of
heat absorption, a CFB boiler may be divided into two regions, the CFB loop and
back-pass
1.1. Primary Loop
The CFB loop includes the furnace, cyclone/impact separator, loop-seal, and
external heat exchanger.
2.2. Secondary Loop or Back-pass
The back-pass is the section of gas pass between the exit of the cyclone/impact
separator and the exit of the air heater. The furnace usually accommodates:
n Evaporator tubes
n Parts of the
superheater
n Parts of or the
entire reheater
The economizer is normally located in the back-pass between the superheater and
the air heater. Evaporator tubes may form the walls of the furnace and those of
the back-pass. Parts of it may also be located in the external heat exchanger.
Sometimes, the superheater tubes also form parts of the back-pass enclosure.
The disposition of the reheater and superheater tubes in the furnace,
back-pass, and external heat exchanger is the designer’s choice. This choice
is, however, influenced by the type of fuel, as shown below. Some designs also
use a steam-cooled cyclone.
