Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) and its Features
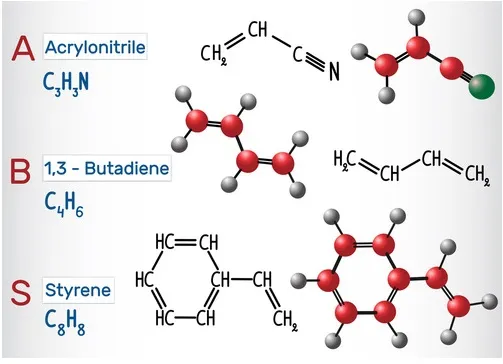
ABS stands for Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene. ABS is an impact-resistant engineering thermoplastic & amorphous polymer. ABS is made up of three monomers: acrylonitrile, butadiene and styrene:
· Acrylonitrile: It is a synthetic monomer produced from propylene and ammonia. This component contributes to ABS chemical resistance & heat stability
· Butadiene: It is produced as a by-product of ethylene production from steam crackers. This component delivers toughness & impact strength to ABS polymer
· Styrene: It is manufactured by dehydrogenation of ethyl benzene. It provides rigidity & processability to ABS plastic

ABS is produced by emulsion or continuous mass technique. The chemical formula of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene is (C8H8·C4H6·C3H3N)n. The natural material is an opaque ivory color and is readily colored with pigments or dyes.
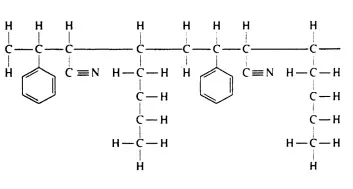
Molecular Structure of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene
ABS is a strong & durable, chemically resistant resin but gets easily attacked by polar solvents. It offers greater impact properties and slightly higher heat distortion temperature than HIPS.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene has a broad processing window and can be processed on most standard machinery. It can be injection-molded, blow-molded, or extruded. It has a low melting temperature making it particularly suitable for processing by 3D printing on an FDM machine.
ABS falls between standard resins (PVC, polyethylene, polystyrene, and so on) and engineering resins (acrylic, nylon acetal…) and often meets the property requirements at a reasonable price-cost effectiveness.
Key suppliers of ABS plastics include: SABIC, RTP Company, LG Chem, Ineos etc. 3D Printing ABS grades are readily available from 3D Systems, Stratasys, Techmer Engineered Solutions…
ABS is an ideal material of choice for various structural applications, thanks to its several physical properties such as:
· High rigidity
· Good impact resistance, even at low temperatures
· Good insulating properties
· Good weldability
· Good abrasion and strain resistance
· High dimensional stability (Mechanically strong and stable over time)
· High surface brightness and excellent surface aspect
ABS shows excellent mechanical properties i.e. it is hard and tough in nature and thus delivers good impact strength. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene offers a high degree of surface quality. Apart from these characteristics, Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene exhibits good electrical insulating properties.
Chemical Properties of ABS
· Very good resistance to diluted acid and alkalis
· Moderate resistance to aliphatic hydrocarbons
· Poor resistance to aromatic hydrocarbons, halogenated Hydrocarbons and alcohols
Elongation at Break | 10 - 50 % |
Elongation at Yield | 1.7 - 6 % |
Flexibility (Flexural Modulus) | 1.6 - 2.4 GPa |
Hardness Shore D | 100 |
Stiffness (Flexural Modulus) | 1.6 - 2.4 GPa |
Strength at Break (Tensile) | 29.8 - 43 MPa |
Strength at Yield (Tensile) | 29.6 - 48 MPa |
Toughness (Notched Izod Impact at Room Temperature) | 200 - 215 J/m |
Toughness at Low Temperature (Notched Izod Impact at Low Temperature) | 20 - 160 J/m |
Young Modulus | 1.79 - 3.2 GPa |
Arc Resistance | 60 - 120 sec |
Dielectric Constant | 2.7 - 3.2 |
Dielectric Strength | 15.7 - 34 kV/mm |
Dissipation Factor | 50 - 190 x 10-4 |
Volume Resistivity | 14 - 16 x 1015 Ohm.cm |
ABS is readily modified both by the addition of additives and by variation of the ratio of the three monomers Acrylonitrile, Butadiene and Styrene. Heat stabilizers, hydrolysis stabilizers, lubricants, UV stabilizers etc. are being used in non-reinforced and reinforced grades to increase specific material properties.
Hence, grades available include:
· High and medium impact
· High heat resistance, and
· Electroplatable
Fire retardant grades can be obtained either by the inclusion of fire retardant additives or by blending with PVC. In order to increase stiffness, impact resistance and dimensional stability, ABS can be reinforced with fibers, fillers, minerals, etc. It can lead to loss on transparency, yield strength...
Limitations of ABS
· Poor weathering resistance
· Ordinary grades burn easily and continue to burn once the flame is removed
· Scratches easily
· Poor solvent resistance, particularly aromatic, ketones and esters
· Can suffer from stress cracking in the presence of some greases
· Low dielectric strength
· Low continuous service temperature