General Definition - III
Eddy Current Testing.
This is a nondestructive testing method in which eddy current flow is induced in the test object. Changes in the flow caused by variations in the object are reflected into a nearby coil or coils for subsequent analysis by suitable instrumentation and techniques.
Edge Joint.
A joint between the edges of two or more parallel or nearly parallel members.
Edge Preparation.
The contour prepared on the edge of a member for welding.
Electric Flash-Welded Pipe.
Pipe having a longitudinal butt joint in which coalescence is produced simultaneously over the entire area of abutting surfaces by the heat obtained from resistance to the flow of electric current between the two surfaces and by the application of pressure after heating is substantially completed. Flashing and upsetting are accompanied by expulsion of metal from the joint.
Electric Fusion-Welded Pipe.
Pipe having a longitudinal or spiral butt joint in which coalescence is produced in the preformed tube by manual or automatic electric arc welding. The weld may be single or double and may be made with or without the use of filler metal.
Electric Resistance-Welded Pipe.
Pipe produced in individual lengths or in continuous lengths from coiled skelp and subsequently cut into individual lengths having a longitudinal butt joint in which coalescence is produced by the heat obtained from resistance of the pipe to the flow of electric current in a circuit of which the pipe is a part and by the application of pressure.
Electrode.
See Covered Electrode. End Preparation. The contour prepared on the end of a pipe, fitting, or nozzle for welding. The particular preparation is prescribed by the governing code.
Engineering Design.
The detailed design developed from process requirements and conforming to established design criteria, including all necessary drawings and specifications, governing a piping installation.
Equipment Connection.
An integral part of such equipment as pressure vessels, heat exchangers, pumps, etc., designed for attachment of pipe or piping components.
Erection.
The complete installation of a piping system, including any field assembly, fabrication, testing, and inspection of the system.
Erosion.
Destruction of materials by the abrasive action of moving fluids, usually accelerated by the presence of solid particles.
Examination.
The procedures for all visual observation and nondestructive testing.
Expansion Joint.
A flexible piping component which absorbs thermal and/or terminal movement.5
Extruded Nozzles.
The forming of nozzle (tee) outlets in pipe by pulling hemispherically or conically shaped dies through a circular hole from the inside of the pipe. Although some cold extruding is done, it is generally performed on steel after the area to be shaped has been heated to temperatures between 2000 and 1600F (1093 and 8710C).
Extruded Pipe.
Pipe produced from hollow or solid round forgings, usually in a hydraulic extrusion press. In this process the forging is contained in a cylindrical die. Initially a punch at the end of the extrusion plunger pierces the forging. The extrusion plunger then forces the contained billet between the cylindrical die and the punch to form the pipe, the latter acting as a mandrel. One variation of this process utilizes autofrettage (hydraulic expansion) and heat treatment, above the recrystallization temperature of the material, to produce a wrought structure.
Fabrication.
Primarily, the joining of piping components into integral pieces ready for assembly. It includes bending, forming, threading, welding, or other operations upon these components, if not part of assembly. It may be done in a shop or in the field.
Face of Weld.
The exposed surface of a weld on the side from which the welding was done.
Filler Metal.
Metal to be added in welding, soldering, brazing, or braze welding.
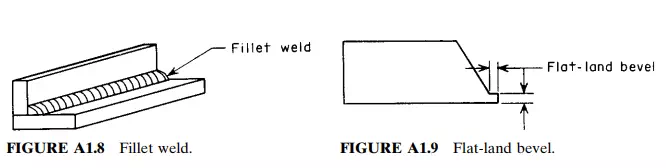
Fillet Weld.
A weld of an approximately triangular cross section joining two surfaces approximately at right angles to each other in a lap joint, tee joint, corner joint, or socket weld. See Fig. A1.8.
Fire Hazard.
Situation in which a material of more than average combustibility or explodibility exists in the presence of a potential ignition source.
Flat-Land Bevel.
A square extended root face preparation extensively used in inert-gas, root-pass welding of piping. See Fig. A1.9.