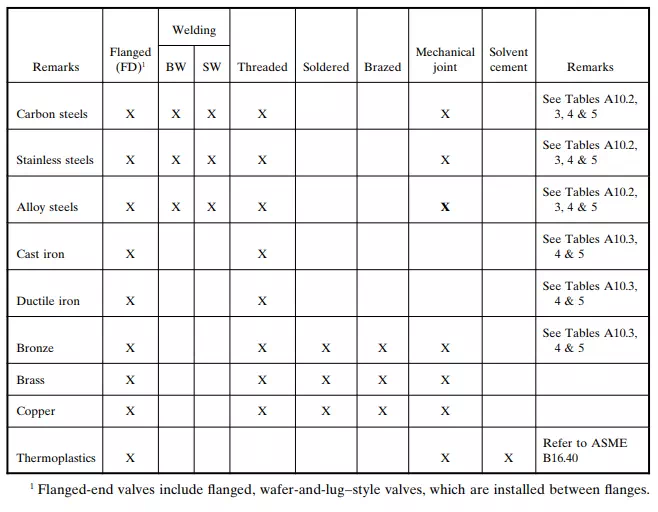
Valves Body Materials and Available End Connections
Bonnet or Cover Bolting.
Bolting includes bolts, nuts, and washers. The bolting to be used must be made from materials acceptable for the application in accordance with the applicable code, standard, specification, or the governing regulation. Refer to the applicable valve standard for acceptable bolting materials.
Disc.
The disc is the part which allows, throttles, or stops flow, depending on its position. In the case of a plug or a ball valve, the disc is called plug or a ball. A valve disc could be cast, forged, or fabricated. A disc is seated against the stationary valve seat or seats when the valve is in the closed position. It can be moved away from the valve seat(s) by motion of the valve stem, with the exception of check and safety-relief valves, in which the disc is moved away from its seat(s) by fluid flow and pressure.
At times some users do not consider the valve disc to be a pressure-retaining or -containing part. The reasoning advanced is that when the valve is in an open position, the disc does not perform a pressure-retaining or -containing functions. However, when the same valve is closed, the disc performs pressure-retaining functions.
Valve Trim.
The removable and replaceable valve internal parts that come in contact with the flow medium are collectively termed as valve trim. These parts include valve seat(s), disc, glands, spacers, guides, bushings, and internal springs. The valve body, bonnet, packing, et cetera that also come in contact with the flow medium are not considered valve trim.