Bund Area To Contain Spillage
The risk of failure of storage tanks and the primary piping systems is reduced to certain extent, if the fluid is contained within the bund wall and is not allowed to spread throughout the area resulting in various hazards like fire, toxic spread, pollution problem etc.
The dyke may be constructed of earth, concrete, solid masonry or steel. It may be square, Rectangular, circular or irregular in shape, conforming to the natural terrain around the tank.
The containment dyke for tankfarm under the purview of chief controller of explosives (CCE) shall be planned according to the CCE rules and regulations. CCE rules are applicable to the fluids of petroleum and petroleum products classified as class A, B or C according to its flash point characteristics.
The rules of CCE can be followed for other hazardous / inflammable products as good guidelines of safety, even though the product is not classified as petroleum product.
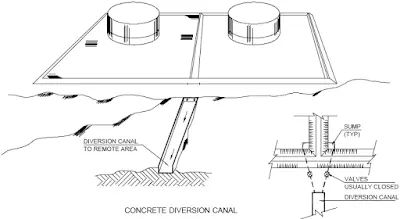
One common method of dyke construction is by earth upto a height of 1.8m and with width of dyke on top to be about 600mm. The slope on the surface of dyke is usually 1:1.5 consistent with the angle of repose of earth.
In congested area or where space is limited, usually concrete dyke is made with varying height for different containment capacity.
The free volume of the bund area is sized to contain the contents of one largest tank plus a margin of 10 percent.
All drains from the dyke area should be equipped with a valve outside the dyke regardless of
whether the drainage goes to disposal pit or sewer system. This prevents liquid spillage from
entering the sewer or released from the dyke area. These valves should be kept closed and blanked off except when withdrawing water.
The contamination of spillage with the natural rain water or wash water needs this drainage to be treated before disposal. Depending on the contamination, the valve can be used for diverting either to storm water system or to the Effluent Treatment Plant.
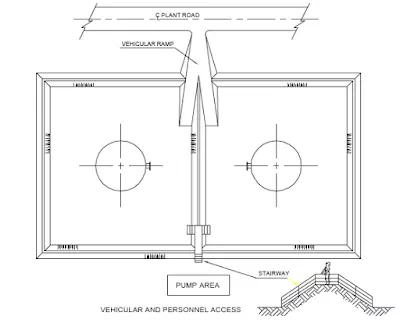
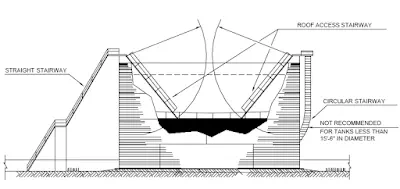
Access to the dyke area is usually provided by making vehicular ramp at one end and a stepped entry at the other end.
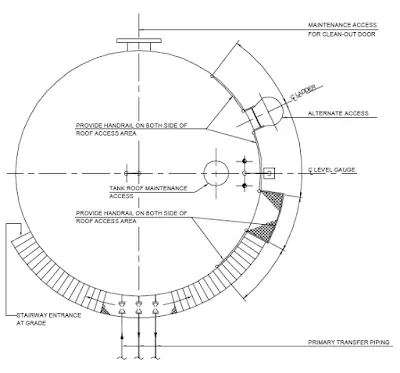
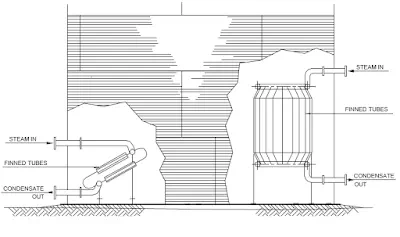
A typical illustration on the top of a vertical storage tank is given in Fig.
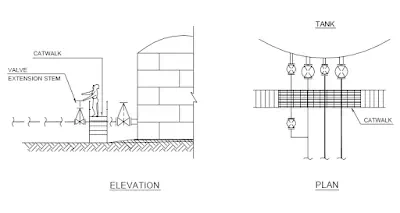
Valve access catwalk, Tank heater installation, Floating Roof Tank access are illustrated as typical examples.
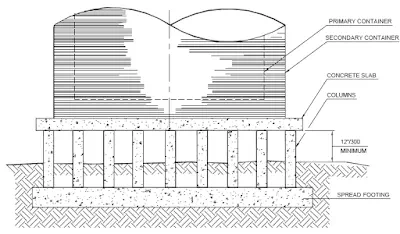
A low temperature tank foundation with elevated concrete base is illustrated in Fig.
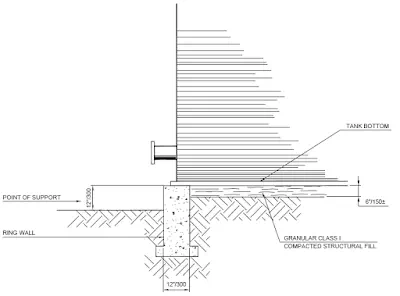
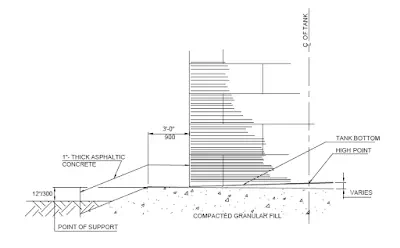
A tank located on compacted granular fill is illustrated in Fig. and a tank on the ring wall
Foundation is illustrated in Fig.