Piping Layout: TankFarm Piping And General Arrangement Drawing Part-1
The study of the tankfarm consisting of a group of tanks shall be carried out keeping the following basic points in consideration.
1. Grouping of tanks,
2. Specification of the content.
3. Capacity of tanks
4. Nature of hazard - fire
- toxic
- explosive
- corrosive
- bulk handling loading
5. unloading
6. Statutory distance
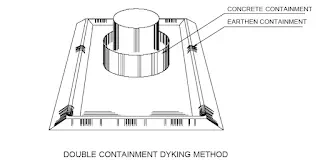
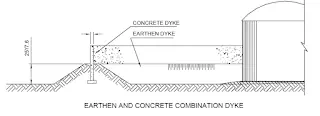
7. Requirement of Dykewall or curbing
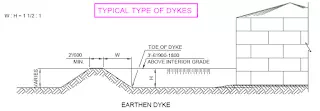
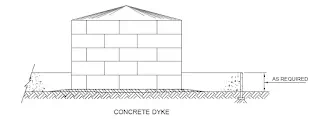
8. Dykewall height or curb height calculation
9. Location of Pumps - inside dyke area
- outside dyke area
10. Approach to tank nozzles with valve
11. Approach to tank roof
12. Drainage of dyke area - Sump and pump
13. Road around tankfarm
14. Fire hydrant / monitor requirement
15. Underground system connected to specific system of treatment / disposal
Storage tanks located in a safe area and grouped according to the contents are called tankfarm. Normally, in chemical plants, the storage shall be either input raw material or output products or intermediate chemicals storage.
Storage tanks may contain acids, alkalis, oil viz. petrol, diesel, naptha, fuel oil or benzene etc. Oil, acid, alkali are usually stored in vertical storage tanks designed as per API 650.
Tanks should be grouped or segregated according to the contents. Tanks containing hydrocarbons should be separated according to the flash point, CCE classification for space planning, dykewall and its height requirement.
Layout of the storage facility shall be based on the following considerations and systematic approach.
- Statutory Regulations viz. CCE
- TAC/NFPA recommendations
- Safety requirements as per OISD, OSHA, HAZOP study
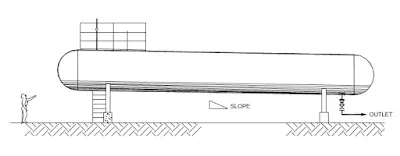
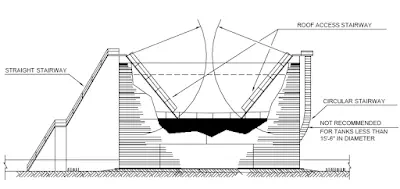
- Valve access platform / ladders at the piping outlet nozzles of tank.
- Access to top of tanks and interconnecting walkway
- Piping on sleepers or piperack inside dyke area.
- Pumps location outside dyke area
The practical objective to prepare a most economical plot plan and piping arrangement for a tankfarm should be to keep provisions of operational ease, maintenance facility, safety arrangements and overall aesthetics. The tankfarm shall also have provisions for efficient drainage and disposal facility as required for various kinds of fluid storage.
The tankfarm should be secured against unauthorised entry by fencing, security gates depending on the tank storage capacity or the type of hazards posed by the nature of contents.
Important Terms Related TankFarm
Atmospheric tank - The tank that operates at pressure levels ranging from atmospheric pressure to 0.5 psig.
Bullet - This is a high pressure horizontal storage vessel shaped like a bullet.
Cone-roof tank - This is a low-pressure vertical storage tank with a cone-shaped fixed roof.
Fixed roof tank - This is a low pressure vertical storage tank with a roof welded to the shell
Irrespective of roof design or method of support.
Floating roof tank - A floating roof tank design is adopted to conserve vapour loss and minimize fire hazard.
Double-wall storage tank - A double wall storage tank has an inner wall to contain a liquid, an
annulus space usually filled with insulation and outerwall for containment of spillage.
Horton sphere - It is a spherical vessel used for storage of high pressure liquid and gases.
Dyke - A dyke is a barrier designed to contain liquid in the tank in case of emergency within the area for safety reasons.
Diversion dyke - This is a barrier designed to divert spillage from other storage tanks. It uses
natural terrain to direct liquids to the sump area.
Flame arrester - In the event of lightning or another source of vapour ignition, a flame arrester in the vent line of a storage tank prevents flames from flashing to the vapour inside the tank.
Breather valve - This is provided as a measure to protect the tank against collapse due to sudden creation of vacuum inside the tank during suction by pumps.
Foot valve - This valve is provided at the bottom of a riser in a tank where a submersible pump can be installed. During regular operation, foot valve remains open.
Sleeper - Sleepers are steel or concrete supports usually located within 450mm of grade of piping systems commonly found in offsites.
Sump - This is the low point basin within an area used for collection of liquid waste for disposal.
Foam - This is a solution with a density lower than that of oil and water. It is used to form a blanket over dangerous vapours and reduce the risk of explosion.