Flexibility Stresses: Code Equations
Flexibility stresses
The piping system experiences different type of stresses when it is installed, tested and in operation. There are different codes according to which the system is designed, each code has different formula for calculating the stress induced in the piping system. Below mentioned are the code equations:
1. ANSI B 31.1 – Power Piping
The Power Piping Code ANSI B 31.1 specifies that the developed stresses due to
sustained, occasional and expansion stresses be calculated in the following
manner.
· 1.1 Sustained
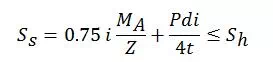
Where, Ss = Sustained stress
i = Stress Intensification factor
MA= Resultant moment due to Primary loads
![]()
Sh = Basic allowable stress at the operating temperature
Z = Stress Intensification factor
· 1.2 Occasional
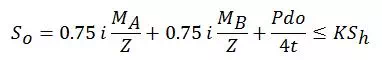
Where, So = Occasional stress
i = Stress Intensification factor
MB = Resultant moment due to occasional loads
![]()
K = Stress Intensification factor
= 1.2 for loads occurring less than 1% of the time
= 1.15 for loads occurring less than 10% of the time
· 1.3 Expansion
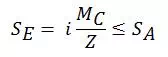
Where, SE = Expansion stress range
MC = Resultant moment due to expansion (Secondary) loads
![]()
SA = Allowable e+xpansion stress range
2. ANSI B 31.3 – Process Piping
· 2.1 Sustained
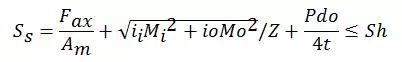
Where, Fax =Axial force due to sustained (primary) loading
Mi =In-plane bending moment due to sustained (primary) loading
Mi = Out-plane bending moment due to sustained (primary) loading
iiio = In-plane & out-plane stress intensification factor
Sh= Basic allowable stress at the operating temperature
· 2.2 Occasional
The code states that calculate the stresses due to sustained and occasional loads independently as per the above equation and then add them absolutely. The sum should not exceed 1.33 Sh.
· 2.3 Expansion
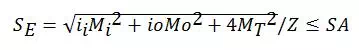
Where, Mi =Range of inplane bending moment due to expansion (secondary) load
Mo = Range of outplane bending moment due to expansion (secondary)load
MT = Range of torsional bending moment due to expansion load
SE = Expansion stress range
SA = Allowable stress range
3. ANSI B 31.4 – Fuel gas piping
The code requires that the sustained, operating, expansion & occasional stresses be calculated and checked as below.
· 3.1 Sustained
![]()
Where, Slp= Longitudinal pressure stress
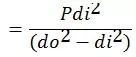
Sb = Bending stress due to sustained loads
· 3.2 Expansion
![]()
Where, Sb = Range of bending stress due to varying loads
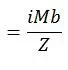
St = Range of torsional stress due to varying loads
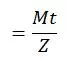
Sy = Specified Minimum Yield stress
· 3.3 Operating
![]()
Where, F = % of axial restraint
= 1 for buried pipe lines
= 0 for above ground pipelines
E = Modulus of Elasticity
a = Thermal expansion coefficient of pipe material
dT= Temperature change from ambient
V = Poisson’s Ratio
SH = Hoop stress =
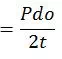
· 3.4 Occasional
![]()
Where, Slp = Longitudinal pressure stress
Sb = Resultant moment due to occasional loads
K = Occasional load factor
4. ANSI B 31.4 – Fuel gas piping
Like B 31.4 code B 31.8 also requires calculations and check of sustained, expansion, operating and occasional stress.
· 4.1 Sustained
![]()
Where, Slp= Longitudinal pressure stress
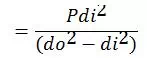
Sb = Bending stress due to sustained loads
Sy = Specified Minimum Yield of pipe material
F = Factor for construction type specified in table 841.114A
T = Temperature derating factor specified in 841.116A
· 4.2 Expansion
![]()
Where, Sb = Bending stress due to varying loads
St = Range of torsional stress due to varying loads
· 4.3 Operating
![]()
· 4.4 Occasional
![]()
Where, K = Occasional load factor