
APPLICATION OF THE REAL GAS EQUATION OF STATE
The determination of the Z−factor as a function of pressure and temperature facilitates the use of the simple equation

to fully define the state of a real gas. This equation is a PVT relationship and in reservoir engineering, in general, the main use of such functions is to relate surface to reservoir volumes of hydrocarbons. For a real gas, in particular, this relation is expressed by the gas expansion factor E, where
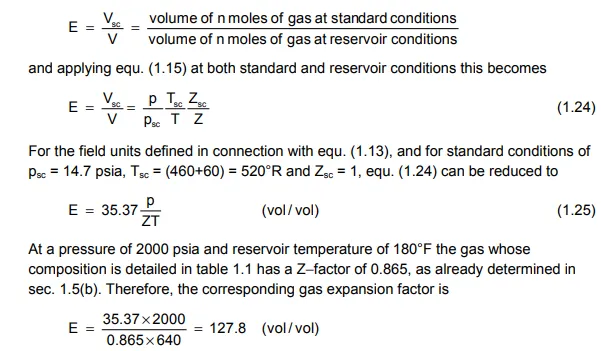
In particular, the gas initially in place (GIIP) in a reservoir can be calculated using an equation which is similar to equ. (1.2) for oil, that is

in which Ei is evaluated at the initial pressure. Other important parameters which can be conveniently expressed using the equation of state are, the real gas density, gravity and isothermal compressibility. Since the mass of n moles of gas is nM, where M is the molecular weight, then the density is

where γg is the gas gravity relative to air at standard conditions and is conventionally expressed as, for instance, γg = 0.8 (air = 1).