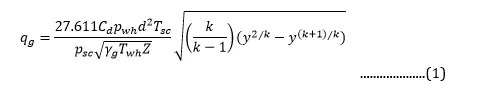
Flow through chokes
A wellhead choke controls the surface pressure and production rate from a well. Chokes usually are selected so that fluctuations in the line pressure downstream of the choke have no effect on the production rate. This requires that flow through the choke be at critical flow conditions. Under critical flow conditions, the flow rate is a function of the upstream or tubing pressure only. For this condition to occur, the downstream pressure must be approximately 0.55 or less of the tubing pressure.
Single-phase gas flow
For single-phase gas flow, Beggs presents Eq. 1, which relates the gas production rate through a choke to the wellhead pressure.
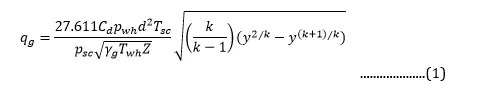
The pressure ratio, y, is the ratio of the downstream pressure to the wellhead pressure. Under critical flow conditions, the pressure ratio is replaced by the critical pressure ratio, yc. The critical pressure ratio is the pressure ratio at which flow becomes critical. This ratio depends on the ratio of the specific heats of the produced gas, as Eq. 2 shows.
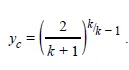 ....................(2)
....................(2)
Two-phase critical flow
Empirical equations have been developed to estimate the relationship between production rate and wellhead pressure for two-phase critical flow. These correlations can be presented in a form similar to Eq. 3.
 ....................(3)
....................(3)
Gilbert was the first to present such a relationship based on field data collected from the Ten Section field of California. Ros and Beggs have also presented relationships that are often used. Table 1 summarizes the parameters for each equation.
Table 1