What Is Plate Tectonics?

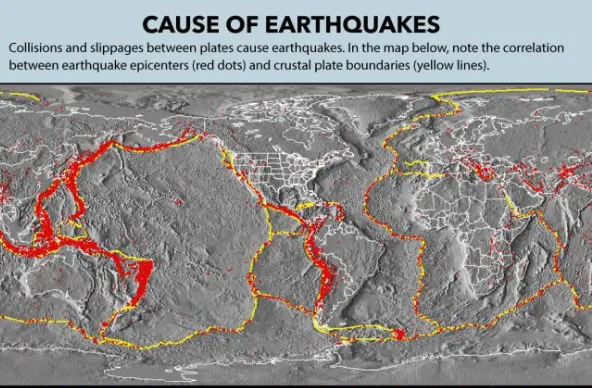
Developed from the 1950s through the 1970s, plate tectonics is the modern version of continental drift, a theory first proposed by scientist Alfred Wegener in 1912. Wegener didn't have an explanation for how continents could move around the planet, but researchers do now. Plate tectonics is the unifying theory of geology, said Nicholas van der Elst, a seismologist at Columbia University's Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory in Palisades, New York.
"Before plate tectonics, people had to come up with explanations of the geologic features in their region that were unique to that particular region," Van der Elst said. "Plate tectonics unified all these descriptions and said that you should be able to describe all geologic features as though driven by the relative motion of these tectonic plates."
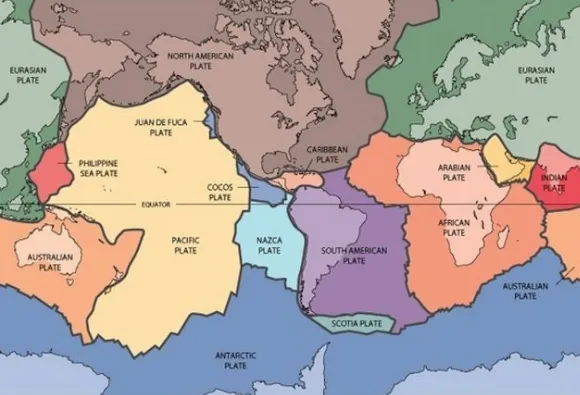
There are nine major plates, according to World Atlas. These plates are named after the landforms found on them. The nine major plates are North American, Pacific, Eurasian, African, Indo-Australian, Australian, Indian, South American and Antarctic.
The largest plate is the Pacific Plate at 39,768,522 square miles (103,000,000 square kilometers). Most of it is located under the ocean. It is moving northwest at a speed of around 2.75 inches (7 cm) per year.
There are also many smaller plates throughout the world.
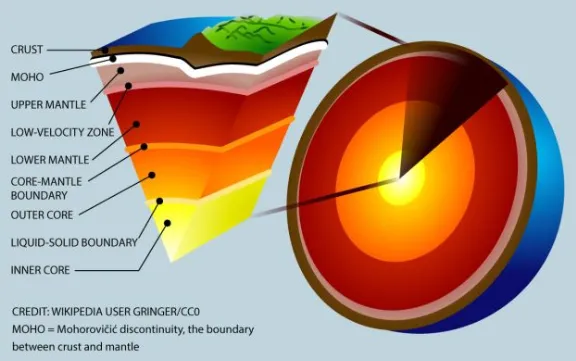
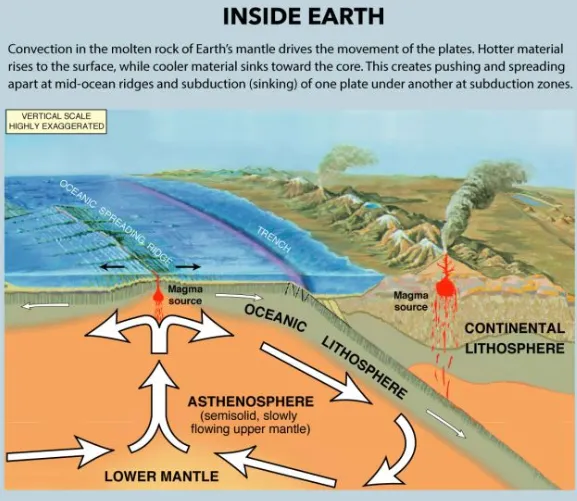
The driving force behind plate tectonics is convection in the mantle. Hot material near the Earth's core rises, and colder mantle rock sinks. "It's kind of like a pot boiling on a stove," Van der Elst said. The convection drive plates tectonics through a combination of pushing and spreading apart at mid-ocean ridges and pulling and sinking downward at subduction zones, researchers think. Scientists continue to study and debate the mechanisms that move the plates.
Mid-ocean ridges are gaps between tectonic plates that mantle the Earth like seams on a baseball. Hot magma wells up at the ridges, forming new ocean crust and shoving the plates apart. At subduction zones, two tectonic plates meet and one slides beneath the other back into the mantle, the layer underneath the crust. The cold, sinking plate pulls the crust behind it downward.
Many spectacular volcanoes are found along subduction zones, such as the "Ring of Fire" that surrounds the Pacific Ocean.
Subduction zones, or convergent margins, are one of the three types of plate boundaries. The others are divergent and transform margins.
At a divergent margin, two plates are spreading apart, as at seafloor-spreading ridges or continental rift zones such as the East Africa Rift.
Transform margins mark slip-sliding plates, such as California's San Andreas Fault, where the North America and Pacific plates grind past each other with a mostly horizontal motion.
While the Earth is 4.54 billion years old, because oceanic crust is constantly recycled at subduction zones, the oldest seafloor is only about 200 million years old. The oldest ocean rocks are found in the northwestern Pacific Ocean and the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Fragments of continental crust are much older, with large chunks at least 3.8 billion years found in Greenland.
With clues left behind in rocks and fossils, geoscientists can reconstruct the past history of Earth's continents. Most researchers think modern plate tectonics began about 3 billion years ago, based on ancient magmas and minerals preserved in rocks from that period. Some believe it could have started a billion years after Earth's birth, at around 3.5 billion years.
"We don't really know when plate tectonics as it looks today got started, but we do know that we have continental crust that was likely scraped off a down-going slab [a tectonic plate in a subduction zone] that is 3.8 billion years old," Van der Elst said. "We could guess that means plate tectonics was operating, but it might have looked very different from today."
As the continents jostle around the Earth, they occasionally come together to form giant supercontinents, a single landmass. One of the earliest big supercontinents, called Rodinia, assembled about 1 billion years ago. Its breakup is linked to a global glaciation called Snowball Earth.
A more recent supercontinent called Pangaea formed about 300 million years ago. Africa, South America, North America and Europe nestled closely together, leaving a characteristic pattern of fossils and rocks for geologists to decipher once Pangaea broke apart. The puzzle pieces left behind by Pangaea, from fossils to the matching shorelines along the Atlantic Ocean, provided the first hints that the Earth's continents move.
Plates bumping into each other can also cause mountain ranges. For example, India and Asia came together about 55 million years ago, which created the Himalaya Mountains, according to National Geographic.